Nanoarchaeum equitans: Perbedaan antara revisi
k Clean up, replaced: selular → seluler using AWB |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.8.5 |
||
| (5 revisi perantara oleh 3 pengguna tidak ditampilkan) | |||
| Baris 10: | Baris 10: | ||
| binomial_authority = Huber et al. 2002 |
| binomial_authority = Huber et al. 2002 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''''Nanoarchaeum equitans''''' adalah spesies [[Archaea]] laut yang ditemukan pada tahun 2002 di [[ventilasi hidrotermal]] di lepas pantai [[Islandia]] pada [[Kolbeinsey]] Ridge oleh [[Karl Stetter]]. Strain |
'''''Nanoarchaeum equitans''''' adalah spesies [[Archaea]] laut yang ditemukan pada tahun 2002 di [[ventilasi hidrotermal]] di lepas pantai [[Islandia]] pada [[Kolbeinsey]] Ridge oleh [[Karl Stetter]]. Strain mikrob ini juga ditemukan pada [[Sub-polar Mid Oceanic Ridge]], dan di [[Obsidian Pool]] di [[Yellowstone National Park]]. Karena tumbuh di suhu mendekati titik didih, sekitar 80 derajat Celcius, itu dianggap [[termofili]]. Hal terbaik tumbuh di lingkungan dengan pH 6, dan konsentrasi salinitas 2%. ''Nanoarchaeum'' tampaknya menjadi [[simbiosis|simbion]] obligat pada arkea ''[[Ignicoccus]]''; itu harus dalam kontak dengan organisme inang untuk bertahan hidup. ''Nanoarchaeum equitans'' tidak dapat mensintesis lipid tetapi memperolehnya dari inangnya. Sel-sel yang hanya 400 [[nanometer|nm]] diameter, menjadikannya salah satu organisme seluler terkecil diketahui, dan dikenal arkea terkecil. |
||
==Lihat pula== |
== Lihat pula == |
||
*[[Archaea]] |
* [[Archaea]] |
||
*[[Candidatus Carsonella ruddii]], [[Rickettsia]], and other [[Proteobacteria]] |
* [[Candidatus Carsonella ruddii]], [[Rickettsia]], and other [[Proteobacteria]] |
||
*[[Ignicoccus]] |
* [[Ignicoccus]] |
||
*[[Mycoplasma]] |
* [[Mycoplasma]] |
||
==Referensi== |
== Referensi == |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
*{{cite journal |last=Huber |first=Harald |authorlink= |display-authors=etal |date=2002 |title=A new phylum of Archaea represented by a nanosized hyperthermophilic symbiont |journal=[[Nature (journal)|Nature]] |volume=417 |issue=6884 |pages=63–67 |doi=10.1038/417063a |url= |accessdate= |quote= |pmid=11986665 }} (This paper represents the first discovery of ''Nanoarchaeum''.) |
* {{cite journal |last=Huber |first=Harald |authorlink= |display-authors=etal |date=2002 |title=A new phylum of Archaea represented by a nanosized hyperthermophilic symbiont |journal=[[Nature (journal)|Nature]] |volume=417 |issue=6884 |pages=63–67 |doi=10.1038/417063a |url= |accessdate= |quote= |pmid=11986665 }} (This paper represents the first discovery of ''Nanoarchaeum''.) |
||
*{{cite journal |last=Waters |first=Elizabeth |authorlink= |display-authors=etal |date=2003 |title=The genome of Nanoarchaeum equitans: insights into early archaeal evolution and derived parasitism |journal=[[Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|PNAS]] |volume=100 |issue=22 |pages=12984–12988 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1735403100 |url= |accessdate= |quote= |pmid=14566062 |pmc=240731 }} (This paper describes the genome sequence of ''Nanoarchaeum''.) |
* {{cite journal |last=Waters |first=Elizabeth |authorlink= |display-authors=etal |date=2003 |title=The genome of Nanoarchaeum equitans: insights into early archaeal evolution and derived parasitism |journal=[[Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|PNAS]] |volume=100 |issue=22 |pages=12984–12988 |doi=10.1073/pnas.1735403100 |url= |accessdate= |quote= |pmid=14566062 |pmc=240731 }} (This paper describes the genome sequence of ''Nanoarchaeum''.) |
||
*{{cite journal |last=Brochier |first=Celine |authorlink= |date=2005 |title=Nanoarchaea: representatives of a novel archaeal phylum or a fast-evolving euryarchaeal lineage related to Thermococcales? |journal=Genome Biology |volume=6 |issue= 5|pages=R42 |doi=10.1186/gb-2005-6-5-r42 |url= |accessdate= |quote= |pmid=15892870 |display-authors=4 |last2=Gribaldo |first2=S |last3=Zivanovic |first3=Y |last4=Confalonieri |first4=F |last5=Forterre |first5=P |pmc=1175954 }} (Recent work suggesting that ''Nanoarchaeum'' is not a new phylum of archaea, but is a type of euryarchaeon.) |
* {{cite journal |last=Brochier |first=Celine |authorlink= |date=2005 |title=Nanoarchaea: representatives of a novel archaeal phylum or a fast-evolving euryarchaeal lineage related to Thermococcales? |journal=Genome Biology |volume=6 |issue= 5|pages=R42 |doi=10.1186/gb-2005-6-5-r42 |url= |accessdate= |quote= |pmid=15892870 |display-authors=4 |last2=Gribaldo |first2=S |last3=Zivanovic |first3=Y |last4=Confalonieri |first4=F |last5=Forterre |first5=P |pmc=1175954 }} (Recent work suggesting that ''Nanoarchaeum'' is not a new phylum of archaea, but is a type of euryarchaeon.) |
||
*{{cite journal |last=Das |first=Sabyasachi |authorlink= |display-authors=etal |date=2006 |title=Analysis of Nanoarchaeum equitans genome and proteome composition: indications for hyperthermophilic and parasitic adaptation |journal=BMC Genomics |volume=7|pages=186 |doi=10.1186/1471-2164-7-186 |url= |accessdate= |quote= |pmid=16869956 |pmc=1574309 }} (This paper describes the genome and proteome analysis of ''Nanoarchaeum''.) |
* {{cite journal |last=Das |first=Sabyasachi |authorlink= |display-authors=etal |date=2006 |title=Analysis of Nanoarchaeum equitans genome and proteome composition: indications for hyperthermophilic and parasitic adaptation |journal=BMC Genomics |volume=7|pages=186 |doi=10.1186/1471-2164-7-186 |url= |accessdate= |quote= |pmid=16869956 |pmc=1574309 }} (This paper describes the genome and proteome analysis of ''Nanoarchaeum''.) |
||
==Bacaan lebih lanjut== |
== Bacaan lebih lanjut == |
||
{{cite journal|last1=Di Giulio|first1=Massimo|title=Is Nanoarchaeum equitans a paleokaryote?|journal=Journal of Biological Research|date=January 1, 2013}} |
{{cite journal|last1=Di Giulio|first1=Massimo|title=Is Nanoarchaeum equitans a paleokaryote?|journal=Journal of Biological Research|date=January 1, 2013}} |
||
==Pranala luar== |
== Pranala luar == |
||
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=192989 NCBI taxonomy page for Nanoarchaeota] |
* [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=192989 NCBI taxonomy page for Nanoarchaeota] |
||
* [http://tolweb.org/Nanoarchaeota/ Tree of Life Nanoarchaeota] |
* [http://tolweb.org/Nanoarchaeota/ Tree of Life Nanoarchaeota] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190912222754/http://tolweb.org/search?taxon=Nanoarchaeota |date=2019-09-12 }} |
||
* [http://www.bacterio.cict.fr/n/nanoarchaeota.html LSPN page for Nanoarchaeota] |
* [http://www.bacterio.cict.fr/n/nanoarchaeota.html LSPN page for Nanoarchaeota]{{Pranala mati|date=Maret 2021 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} |
||
* [http://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Nanoarchaeum MicrobeWiki page for Nanoarchaeum] |
* [http://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Nanoarchaeum MicrobeWiki page for Nanoarchaeum] |
||
{{Taxonbar|from=Q221936}} |
|||
[[Kategori:Arkea]] |
[[Kategori:Arkea]] |
||
[[Kategori:Organisms living on hydrothermal vents]] |
|||
Revisi terkini sejak 26 Desember 2021 20.48
| Nanoarchaeum equitans | |
|---|---|
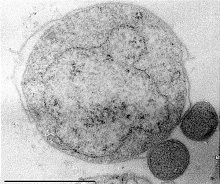
| |
| Nanoarchaeum equitans (dan inangnya Ignicoccus) | |
| Klasifikasi ilmiah | |
| Domain: | |
| Filum: | |
| Genus: | |
| Spesies: | N. equitans
|
| Nama binomial | |
| Nanoarchaeum equitans Huber et al. 2002
| |
Nanoarchaeum equitans adalah spesies Archaea laut yang ditemukan pada tahun 2002 di ventilasi hidrotermal di lepas pantai Islandia pada Kolbeinsey Ridge oleh Karl Stetter. Strain mikrob ini juga ditemukan pada Sub-polar Mid Oceanic Ridge, dan di Obsidian Pool di Yellowstone National Park. Karena tumbuh di suhu mendekati titik didih, sekitar 80 derajat Celcius, itu dianggap termofili. Hal terbaik tumbuh di lingkungan dengan pH 6, dan konsentrasi salinitas 2%. Nanoarchaeum tampaknya menjadi simbion obligat pada arkea Ignicoccus; itu harus dalam kontak dengan organisme inang untuk bertahan hidup. Nanoarchaeum equitans tidak dapat mensintesis lipid tetapi memperolehnya dari inangnya. Sel-sel yang hanya 400 nm diameter, menjadikannya salah satu organisme seluler terkecil diketahui, dan dikenal arkea terkecil.
Lihat pula
[sunting | sunting sumber]Referensi
[sunting | sunting sumber]- Huber, Harald; et al. (2002). "A new phylum of Archaea represented by a nanosized hyperthermophilic symbiont". Nature. 417 (6884): 63–67. doi:10.1038/417063a. PMID 11986665. (This paper represents the first discovery of Nanoarchaeum.)
- Waters, Elizabeth; et al. (2003). "The genome of Nanoarchaeum equitans: insights into early archaeal evolution and derived parasitism". PNAS. 100 (22): 12984–12988. doi:10.1073/pnas.1735403100. PMC 240731
 . PMID 14566062. (This paper describes the genome sequence of Nanoarchaeum.)
. PMID 14566062. (This paper describes the genome sequence of Nanoarchaeum.) - Brochier, Celine; Gribaldo, S; Zivanovic, Y; Confalonieri, F; et al. (2005). "Nanoarchaea: representatives of a novel archaeal phylum or a fast-evolving euryarchaeal lineage related to Thermococcales?". Genome Biology. 6 (5): R42. doi:10.1186/gb-2005-6-5-r42. PMC 1175954
 . PMID 15892870. (Recent work suggesting that Nanoarchaeum is not a new phylum of archaea, but is a type of euryarchaeon.)
. PMID 15892870. (Recent work suggesting that Nanoarchaeum is not a new phylum of archaea, but is a type of euryarchaeon.) - Das, Sabyasachi; et al. (2006). "Analysis of Nanoarchaeum equitans genome and proteome composition: indications for hyperthermophilic and parasitic adaptation". BMC Genomics. 7: 186. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-7-186. PMC 1574309
 . PMID 16869956. (This paper describes the genome and proteome analysis of Nanoarchaeum.)
. PMID 16869956. (This paper describes the genome and proteome analysis of Nanoarchaeum.)
Bacaan lebih lanjut
[sunting | sunting sumber]Di Giulio, Massimo (January 1, 2013). "Is Nanoarchaeum equitans a paleokaryote?". Journal of Biological Research.
