Satuan astronomi: Perbedaan antara revisi
k bot Menambah: ka:ასტრონომიული ერთეული |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.8.9 |
||
| (43 revisi perantara oleh 24 pengguna tidak ditampilkan) | |||
| Baris 1: | Baris 1: | ||
{{disambiginfo|AU|AU}} |
{{disambiginfo|AU|AU}} |
||
{{Infobox unit |
|||
'''Satuan astronomi''' - '''SA''' ([[bahasa Inggris]]: '''Astronomical unit''', '''AU''') adalah sebuah satuan [[jarak]], kira-kira sama dengan jarak antara [[Bumi]] dan [[Matahari]]. Nilai dari SA yang diterima umum adalah 149 597 870 691 ± 30 meter (sekitar 150 juta kilometer atau 93 juta mil). |
|||
| bgcolour = |
|||
| name = Satuan astronomi |
|||
| image= [[Berkas:Astronomical unit.png|200px]] |
|||
| caption= Garis abu-abu menunjukkan jarak Bumi-Matahari, yang rata-ratanya sekitar 1 satuan astronomi. |
|||
| standard = [[:en:Astronomical system of units|Sistem satuan astronomi]] |
|||
| quantity = [[panjang]] |
|||
| symbol = au, ua, atau AU |
|||
| units1 =Satuan [[sistem metrik|metrik]] ([[Sistem Satuan Internasional|SI]]) |
|||
| inunits1 = {{val|149597870700|ul=m}} |
|||
| units2 =Satuan [[Satuan imperial|imperial]] & [[:en:United States customary units|AS]] |
|||
| inunits2 ={{val|9.2956|e=7|ul=mi}} |
|||
| units3 = [[:en:Astronomical system of units|unit astronomi]] |
|||
| inunits3 = {{val|4.8481|e=-6|ul=pc}}<br /> {{val|1.5813|e=-5|ul=ly}} |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Satuan astronomi''', disingkat '''sa''' ([[bahasa Inggris]]: '''''astronomical unit''''', [[satuan internasional|SI]]: '''au''') adalah sebuah satuan [[jarak]], kira-kira sama dengan jarak antara [[Bumi]] dan [[Matahari]]. Nilai dari ''sa'' yang diterima umum adalah 149.597.870,691 ± 30 meter (sekitar 150 juta kilometer atau 93 juta mil |
|||
Beberapa konversi: |
Beberapa konversi: |
||
* 1 |
* 1 sa = 149.597.870,691 ± 0,030 km ≈ 92 955 807 mil ≈ 8,317 [[tahun cahaya|menit cahaya]] ≈ 499 [[detik cahaya]] |
||
* 1 [[jam-cahaya]] ≈ 7,214 |
* 1 [[jam-cahaya]] ≈ 7,214 au |
||
* 1 [[hari-cahaya]] ≈ 173 |
* 1 [[hari-cahaya]] ≈ 173 au |
||
* 1 [[tahun-cahaya]] ≈ 63.241 |
* 1 [[tahun-cahaya]] ≈ 63.241 au |
||
* 1 [[parsec|pc]] ≈ 206.265 |
* 1 [[parsec|pc]] ≈ 206.265 au |
||
== Sejarah penggunaan simbol == |
|||
Berbagai simbol satuan dan singkatan telah digunakan untuk satuan astronomi. Dalam resolusi 1976, [[Persatuan Astronomi Internasional]] (IAU) menggunakan simbol A untuk satuan astronomi.<ref name="IAU76">Resolution No. 10 of the [http://www.iau.org/static/resolutions/IAU1976_French.pdf XVIth General Assembly of the International Astronomical Union], Grenoble, 1976</ref> Dalam literatur astronomi, simbol AU adalah (dan tetap) umum. Pada tahun 2006, [[Biro Internasional untuk Ukuran dan Timbangan]] (BIPM) merekomendasikan ua sebagai simbol untuk satuan ini.<ref name="Bureau International des Poids et Mesures 2006 126">{{Citation |author=Bureau International des Poids et Mesures | author-link = Bureau International des Poids et Mesures |title=The International System of Units (SI) |place= |publisher=Organisation Intergouvernementale de la Convention du Mètre |date=2006 |edition=8th |page=126 |url=http://www.bipm.org/utils/common/pdf/si_brochure_8_en.pdf}}</ref> Dalam Lampiran C non-normatif untuk [[ISO 80000-3]] (2006), simbol satuan astronomi adalah "ua". Pada tahun 2012, IAU, mencatat "bahwa berbagai simbol saat ini digunakan untuk satuan astronomi", merekomendasikan penggunaan simbol "au".<ref name="IAUresB2">{{citation |contribution=RESOLUTION B2 on the re-definition of the astronomical unit of length |title=RESOLUTION B2 | editor-last = International Astronomical Union |publisher=[[International Astronomical Union]] |place=Beijing, China |date=31 August 2012 | contribution-url = http://www.iau.org/static/resolutions/IAU2012_English.pdf |quote=The XXVIII General Assembly of International Astronomical Union … recommends … 5. that the unique symbol "au" be used for the astronomical unit.}}</ref> Dalam revisi 2014 Brosur SI, BIPM menggunakan simbol satuan "au".<ref name="AAS_style">{{cite web | url=http://aas.org/authors/manuscript-preparation-aj-apj-author-instructions#_Toc2.2 | title=Manuscript Preparation: AJ & ApJ Author Instructions | website=American Astronomical Society | accessdate=29 October 2016 | quote="Use standard abbreviations for SI... and natural units (e.g., au, pc, cm)." | archive-date=2018-12-25 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181225010956/https://journals.aas.org/manuscript-preparation/#_Toc2.2 | dead-url=yes }}</ref><ref name=SI_Brochure2012>{{cite web |url=http://www.bipm.org/en/publications/si-brochure/table6.html |title=SI Brochure: The International System of Units (SI) [8th edition, 2006; updated in 2014] |publisher=BIPM |date=2014 |accessdate=3 January 2015}}</ref> |
|||
== Perkembangan == |
|||
[[Berkas:Stellarparallax parsec1.svg|jmpl|ka|''Satuan astronomi'' digunakan sebagai garis dasar segitiga untuk mengukur [[paralaks bintang]] ''(jarak dalam gambar tidak menurut skala)''.]] |
|||
Satuan jarak ''A'' (nilai satuan astronomi dalam meter) dapat dinyatakan dalam [[konstanta astronomi]] lainnya: |
|||
:<math>A^3 = \frac{G M_\odot D^2}{k^2}</math> |
|||
di mana ''G'' adalah [[konstanta gravitasi Newton]], {{solar mass}} adalah [[massa matahari]], ''k'' adalah nilai numerik dari [[konstanta gravitasi Gauss]] dan ''D'' adalah periode waktu satu hari. |
|||
== Contoh == |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style=" width: 690px; font-size: 0.9em;" |
|||
|- |
|||
! width= 100 | Objek |
|||
! width= 80 | Panjang atau jarak (AU) |
|||
! width= 50 class="unsortable"| Jangkauan |
|||
! class="unsortable" | Keterangan dan titik acuan |
|||
! width= 25 class="unsortable" | Ref |
|||
|- style="background-color: #e2e2e2" |
|||
| align=left | [[Detik-cahaya]] |
|||
| align=right| 0,002<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu detik |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Jarak bulan (astronomi)|Jarak bulan]] |
|||
| align=right| 0,0026 |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak rata-rata dari Bumi |
|||
| – |
|||
|- style="background-color: #e2e2e2" |
|||
| align=left | [[Radius matahari]] |
|||
| align=right| 0,005<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jari-jari [[Matahari]] ({{val|695500|u=km}}, {{val|432450|u=mil}}, seratus kali jari-jari Bumi atau sepuluh kali jari-jari rata-rata Jupiter) |
|||
| – |
|||
|- style="background-color: #e2e2e2" |
|||
| align=left | [[Menit-cahaya]] |
|||
| align=right| 0,12<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu menit |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Merkurius]] |
|||
| align=right| 0,39<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak rata-rata dari Matahari |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Venus]] |
|||
| align=right| 0,72<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak rata-rata dari Matahari |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Bumi]] |
|||
| align=right| 1,00<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak rata-rata [[orbit Bumi]] dari Matahari ([[sinar matahari]] bergerak selama 8 menit dan 19 detik sebelum mencapai Bumi) |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Mars]] |
|||
| align=right| 1,52<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak rata-rata dari Matahari |
|||
| – |
|||
|- style="background-color: #e2e2e2" |
|||
| align=left | [[Detik-cahaya#Penggunaan dalam astronomi|Jam-cahaya]] |
|||
| align=right| 7,2<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu jam |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Sabuk Kuiper]] |
|||
| align=right| 30<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | Tepi bagian dalam dimulai sekitar 30 AU |
|||
|<ref>{{Citation |url=http://www.iop.org/EJ/article/0004-637X/490/2/879/36659.html |author=Alan Stern |title=Collisional Erosion in the Primordial Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt and the Generation of the 30–50 AU Kuiper Gap |journal=The Astrophysical Journal |volume=490 |issue=2 |pages=879–882 |date=1997 |doi=10.1086/304912 |last2=Colwell |first2=Joshua E. |bibcode=1997ApJ...490..879S |postscript=. |accessdate=2019-01-02 |archive-date=2020-03-25 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200325122837/http://www.iop.org/EJ/article/0004-637X/490/2/879/36659.html |dead-url=yes }}</ref> |
|||
|- style="background-color: #e2e2e2" |
|||
| align=left | [[Hari-cahaya]] |
|||
| align=right| 173<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu hari |
|||
| – |
|||
|- style="background-color: #e2e2e2" |
|||
| align=left | [[Tahun-cahaya]] |
|||
| align=right| {{val|63241}}<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu [[tahun Julian]] (365,25 hari) |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Awan Oort]] |
|||
| align=right| {{val|75000}}<!--figure space --> |
|||
| ± {{val|25000}} |
|||
| align=left | jarak batas terluar awan Oort dari Matahari (diperkirakan, sama dengan 1,2 tahun cahaya) |
|||
| – |
|||
|- style="background-color: #e2e2e2" |
|||
| align=left | [[Parsec]] |
|||
| align=right| {{val|206265}}<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | satu [[parsec]] (Parsec didefinisikan berdasarkan satuan astronomi, digunakan untuk mengukur jarak di luar Tata Surya dan sekitar 3,26 tahun cahaya.) |
|||
|<ref>http://www.iau.org, [http://www.iau.org/public/themes/measuring/ Measuring the Universe–The IAU and astronomical units]</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Proxima Centauri]] |
|||
| align=right| {{val|268000}}<!--figure space --> |
|||
| ± 126 |
|||
| align=left | jarak dari Tata Surya ke bintang terdekat |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
| align=left | [[Pusat Galaksi]] |
|||
| align=right| {{val|1700000000}}<!--figure space --> |
|||
| – |
|||
| align=left | jarak dari Matahari ke pusat [[Bima Sakti]] |
|||
| – |
|||
|- |
|||
! colspan=5 style="font-weight: normal; font-size: 0.9em; text-align: left; padding: 6px 2px 4px 4px" | Catatan: angka-angka dalam tabel ini umumnya pembulatan, perkiraan, sering kali perkiraan kasar, dan mungkin sangat berbeda dari sumber lain. Tabel juga mencakup satuan panjang lain untuk perbandingan. |
|||
|} |
|||
== Lihat pula == |
== Lihat pula == |
||
* [[parsec]] dan [[tahun cahaya]], |
* [[parsec]] dan [[tahun cahaya]], |
||
* [[jarak astronomis]] |
* [[jarak astronomis]] |
||
* [[konversi satuan]], |
* [[konversi satuan]], |
||
* [[urutan besaran]] |
* [[urutan besaran]] |
||
== Referensi == |
== Referensi == |
||
{{reflist}} |
|||
* E. Myles Standish. "Report of the IAU WGAS Sub-group on Numerical Standards". In ''Highlights of Astronomy'', I. Appenzeller, ed. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1995. ''(Complete report available online: [http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/iau-comm4/iausgnsrpt.ps PostScript]. Tables from the report also available: [http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/astro_constants.html Astrodynamic Constants and Parameters])'' |
* E. Myles Standish. "Report of the IAU WGAS Sub-group on Numerical Standards". In ''Highlights of Astronomy'', I. Appenzeller, ed. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1995. ''(Complete report available online: [http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/iau-comm4/iausgnsrpt.ps PostScript] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060208115515/http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/iau-comm4/iausgnsrpt.ps |date=2006-02-08 }}. Tables from the report also available: [http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/astro_constants.html Astrodynamic Constants and Parameters])'' |
||
* D. D. McCarthy ed., IERS Conventions (1996), IERS Technical Note 21, Observatoire de Paris, July 1996 |
* D. D. McCarthy ed., IERS Conventions (1996), IERS Technical Note 21, Observatoire de Paris, July 1996 |
||
* {{en}} Yeomans D. Astronomical Unit (AU). 2011. [http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/glossary/au.html]{{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130606123702/http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/glossary/au.html |date=2013-06-06 }} <small>Diakses tanggal 31 Mei 2011</small> |
|||
== Pranala luar == |
== Pranala luar == |
||
* {{en}} [http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/outside.html Units outside the SI] |
* {{en}} [http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/outside.html Units outside the SI] |
||
* {{en}} [http://www.iau.org/IAU/Activities/nomenclature/units.html Recommendations concerning Units] |
* {{en}} [http://www.iau.org/IAU/Activities/nomenclature/units.html Recommendations concerning Units] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060620111248/http://www.iau.org/IAU/Activities/nomenclature/units.html |date=2006-06-20 }} |
||
* {{en}} [http://home.comcast.net/~pdnoerd/SMassLoss.html Solar Mass Loss, the Astronomical Unit, and the Scale of the Solar System] |
* {{en}} [http://home.comcast.net/~pdnoerd/SMassLoss.html Solar Mass Loss, the Astronomical Unit, and the Scale of the Solar System] |
||
* {{en}} [http://www.ex.ac.uk/trol/scol/ccleng.htm Conversion Calculator for Units of LENGTH] |
* {{en}} [http://www.ex.ac.uk/trol/scol/ccleng.htm Conversion Calculator for Units of LENGTH] |
||
{{Satuan SI}} |
|||
{{satuan-stub}} |
{{satuan-stub}} |
||
[[Kategori:Jarak astronomis]] |
[[Kategori:Jarak astronomis]] |
||
[[Kategori:Satuan panjang]] |
|||
[[Kategori:Mekanika benda langit]] |
|||
[[als:Astronomische Einheit]] |
|||
[[ar:وحدة فلكية]] |
|||
[[ast:Unidá astronómica]] |
|||
[[az:Astronomik Vahid]] |
|||
[[be:Астранамічная адзінка]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Астранамічная адзінка]] |
|||
[[bg:Астрономическа единица]] |
|||
[[bn:জ্যোতির্বিদ্যা-একক]] |
|||
[[br:Unanenn astronomek]] |
|||
[[bs:Astronomska jedinica]] |
|||
[[ca:Unitat astronòmica]] |
|||
[[cs:Astronomická jednotka]] |
|||
[[cy:Uned seryddol]] |
|||
[[da:Astronomisk enhed]] |
|||
[[de:Astronomische Einheit]] |
|||
[[el:Αστρονομική μονάδα]] |
|||
[[en:Astronomical unit]] |
|||
[[eo:Astronomia unuo]] |
|||
[[es:Unidad astronómica]] |
|||
[[et:Astronoomiline ühik]] |
|||
[[eu:Unitate astronomiko]] |
|||
[[fa:واحد نجومی]] |
|||
[[fi:Astronominen yksikkö]] |
|||
[[fr:Unité astronomique]] |
|||
[[ga:Aonad réalteolaíoch]] |
|||
[[gl:Unidade astronómica]] |
|||
[[gv:Unnid rollageagh]] |
|||
[[he:יחידה אסטרונומית]] |
|||
[[hi:खगोलीय इकाई]] |
|||
[[hr:Astronomska jedinica]] |
|||
[[hu:Csillagászati egység]] |
|||
[[io:Astronomiala unajo]] |
|||
[[is:Stjarnfræðieining]] |
|||
[[it:Unità Astronomica]] |
|||
[[ja:天文単位]] |
|||
[[ka:ასტრონომიული ერთეული]] |
|||
[[kk:Астрономиялық бірлік]] |
|||
[[kn:ಖಗೋಳ ಮಾನ]] |
|||
[[ko:천문단위]] |
|||
[[la:Unitas astronomica]] |
|||
[[lb:Astronomesch Eenheet]] |
|||
[[lt:Astronominis vienetas]] |
|||
[[lv:Astronomiskā vienība]] |
|||
[[ml:സൗരദൂരം]] |
|||
[[mn:Одон орны нэгж]] |
|||
[[mr:खगोलीय एकक]] |
|||
[[ms:Unit astronomi]] |
|||
[[nds:Astronoomsch Eenheit]] |
|||
[[nl:Astronomische eenheid]] |
|||
[[nn:Astronomisk eining]] |
|||
[[no:Astronomisk enhet]] |
|||
[[pl:Jednostka astronomiczna]] |
|||
[[pms:Unità Astronòmica]] |
|||
[[pt:Unidade astronômica]] |
|||
[[ro:Unitate astronomică]] |
|||
[[ru:Астрономическая единица]] |
|||
[[scn:Unità astrunòmica]] |
|||
[[simple:Astronomical unit]] |
|||
[[sk:Astronomická jednotka]] |
|||
[[sl:Astronomska enota]] |
|||
[[sr:Астрономска јединица]] |
|||
[[sv:Astronomisk enhet]] |
|||
[[ta:வானியல் அலகு]] |
|||
[[th:หน่วยดาราศาสตร์]] |
|||
[[tr:Astronomik birim]] |
|||
[[uk:Астрономічна одиниця довжини]] |
|||
[[uz:Astronomik birlik]] |
|||
[[vi:Đơn vị thiên văn]] |
|||
[[zh:天文單位]] |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Thian-bûn tan-ūi]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:天文單位]] |
|||
Revisi terkini sejak 2 Agustus 2022 13.04
| Satuan astronomi | |
|---|---|
 Garis abu-abu menunjukkan jarak Bumi-Matahari, yang rata-ratanya sekitar 1 satuan astronomi. | |
| Informasi umum | |
| Sistem satuan astronomi | |
| Besaran | panjang |
| Simbol | au, ua, atau AU |
| Konversi | |
| 1 au, ua, atau AU dalam ... | ... sama dengan ... |
| Satuan metrik (SI) | 149.597.870.700 m |
| Satuan imperial & AS | 9,2956×107 mi |
| unit astronomi | 4,8481×10−6 pc 1,5813×10−5 ly |
Satuan astronomi, disingkat sa (bahasa Inggris: astronomical unit, SI: au) adalah sebuah satuan jarak, kira-kira sama dengan jarak antara Bumi dan Matahari. Nilai dari sa yang diterima umum adalah 149.597.870,691 ± 30 meter (sekitar 150 juta kilometer atau 93 juta mil
Beberapa konversi:
- 1 sa = 149.597.870,691 ± 0,030 km ≈ 92 955 807 mil ≈ 8,317 menit cahaya ≈ 499 detik cahaya
- 1 jam-cahaya ≈ 7,214 au
- 1 hari-cahaya ≈ 173 au
- 1 tahun-cahaya ≈ 63.241 au
- 1 pc ≈ 206.265 au
Sejarah penggunaan simbol
[sunting | sunting sumber]Berbagai simbol satuan dan singkatan telah digunakan untuk satuan astronomi. Dalam resolusi 1976, Persatuan Astronomi Internasional (IAU) menggunakan simbol A untuk satuan astronomi.[1] Dalam literatur astronomi, simbol AU adalah (dan tetap) umum. Pada tahun 2006, Biro Internasional untuk Ukuran dan Timbangan (BIPM) merekomendasikan ua sebagai simbol untuk satuan ini.[2] Dalam Lampiran C non-normatif untuk ISO 80000-3 (2006), simbol satuan astronomi adalah "ua". Pada tahun 2012, IAU, mencatat "bahwa berbagai simbol saat ini digunakan untuk satuan astronomi", merekomendasikan penggunaan simbol "au".[3] Dalam revisi 2014 Brosur SI, BIPM menggunakan simbol satuan "au".[4][5]
Perkembangan
[sunting | sunting sumber]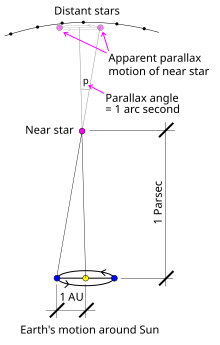
Satuan jarak A (nilai satuan astronomi dalam meter) dapat dinyatakan dalam konstanta astronomi lainnya:
di mana G adalah konstanta gravitasi Newton, M☉ adalah massa matahari, k adalah nilai numerik dari konstanta gravitasi Gauss dan D adalah periode waktu satu hari.
Contoh
[sunting | sunting sumber]| Objek | Panjang atau jarak (AU) | Jangkauan | Keterangan dan titik acuan | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detik-cahaya | 0,002 | – | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu detik | – |
| Jarak bulan | 0,0026 | – | jarak rata-rata dari Bumi | – |
| Radius matahari | 0,005 | – | jari-jari Matahari (695.500 km, 432.450 mi, seratus kali jari-jari Bumi atau sepuluh kali jari-jari rata-rata Jupiter) | – |
| Menit-cahaya | 0,12 | – | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu menit | – |
| Merkurius | 0,39 | – | jarak rata-rata dari Matahari | – |
| Venus | 0,72 | – | jarak rata-rata dari Matahari | – |
| Bumi | 1,00 | – | jarak rata-rata orbit Bumi dari Matahari (sinar matahari bergerak selama 8 menit dan 19 detik sebelum mencapai Bumi) | – |
| Mars | 1,52 | – | jarak rata-rata dari Matahari | – |
| Jam-cahaya | 7,2 | – | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu jam | – |
| Sabuk Kuiper | 30 | – | Tepi bagian dalam dimulai sekitar 30 AU | [6] |
| Hari-cahaya | 173 | – | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu hari | – |
| Tahun-cahaya | 63.241 | – | jarak yang ditempuh cahaya dalam satu tahun Julian (365,25 hari) | – |
| Awan Oort | 75.000 | ± 25.000 | jarak batas terluar awan Oort dari Matahari (diperkirakan, sama dengan 1,2 tahun cahaya) | – |
| Parsec | 206.265 | – | satu parsec (Parsec didefinisikan berdasarkan satuan astronomi, digunakan untuk mengukur jarak di luar Tata Surya dan sekitar 3,26 tahun cahaya.) | [7] |
| Proxima Centauri | 268.000 | ± 126 | jarak dari Tata Surya ke bintang terdekat | – |
| Pusat Galaksi | 1.700.000.000 | – | jarak dari Matahari ke pusat Bima Sakti | – |
| Catatan: angka-angka dalam tabel ini umumnya pembulatan, perkiraan, sering kali perkiraan kasar, dan mungkin sangat berbeda dari sumber lain. Tabel juga mencakup satuan panjang lain untuk perbandingan. | ||||
Lihat pula
[sunting | sunting sumber]Referensi
[sunting | sunting sumber]- ^ Resolution No. 10 of the XVIth General Assembly of the International Astronomical Union, Grenoble, 1976
- ^ Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (2006), The International System of Units (SI) (PDF) (edisi ke-8th), Organisation Intergouvernementale de la Convention du Mètre, hlm. 126
- ^ International Astronomical Union, ed. (31 August 2012), "RESOLUTION B2 on the re-definition of the astronomical unit of length" (PDF), RESOLUTION B2, Beijing, China: International Astronomical Union,
The XXVIII General Assembly of International Astronomical Union … recommends … 5. that the unique symbol "au" be used for the astronomical unit.
- ^ "Manuscript Preparation: AJ & ApJ Author Instructions". American Astronomical Society. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 2018-12-25. Diakses tanggal 29 October 2016.
Use standard abbreviations for SI... and natural units (e.g., au, pc, cm).
- ^ "SI Brochure: The International System of Units (SI) [8th edition, 2006; updated in 2014]". BIPM. 2014. Diakses tanggal 3 January 2015.
- ^ Alan Stern; Colwell, Joshua E. (1997), "Collisional Erosion in the Primordial Edgeworth-Kuiper Belt and the Generation of the 30–50 AU Kuiper Gap", The Astrophysical Journal, 490 (2): 879–882, Bibcode:1997ApJ...490..879S, doi:10.1086/304912, diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 2020-03-25, diakses tanggal 2019-01-02.
- ^ http://www.iau.org, Measuring the Universe–The IAU and astronomical units
- E. Myles Standish. "Report of the IAU WGAS Sub-group on Numerical Standards". In Highlights of Astronomy, I. Appenzeller, ed. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1995. (Complete report available online: PostScript Diarsipkan 2006-02-08 di Wayback Machine.. Tables from the report also available: Astrodynamic Constants and Parameters)
- D. D. McCarthy ed., IERS Conventions (1996), IERS Technical Note 21, Observatoire de Paris, July 1996
- (Inggris) Yeomans D. Astronomical Unit (AU). 2011. [1]Diarsipkan 2013-06-06 di Wayback Machine. Diakses tanggal 31 Mei 2011
Pranala luar
[sunting | sunting sumber]- (Inggris) Units outside the SI
- (Inggris) Recommendations concerning Units Diarsipkan 2006-06-20 di Wayback Machine.
- (Inggris) Solar Mass Loss, the Astronomical Unit, and the Scale of the Solar System
- (Inggris) Conversion Calculator for Units of LENGTH


