Lepton: Perbedaan antara revisi
Wagino Bot (bicara | kontrib) k →Pranala: minor cosmetic change |
k Bot: Mengganti kategori yang dialihkan Konsep fisika dasar menjadi Konsep dalam fisika |
||
| (8 revisi perantara oleh 5 pengguna tidak ditampilkan) | |||
| Baris 2: | Baris 2: | ||
| bgcolour = |
| bgcolour = |
||
| name = Lepton |
| name = Lepton |
||
| image = [[ |
| image = [[Berkas:Beta Negative Decay.svg|200px]] |
||
| caption = Lepton terlibat dalam beberapa proses seperti [[peluruhan beta]]. |
| caption = Lepton terlibat dalam beberapa proses seperti [[peluruhan beta]]. |
||
| num_types = 6 ([[elektron]], [[neutrino elektron]], [[muon]], [[neutrino muon]], [[tau (partikel)|tau]], [[neutrino tau]]) |
| num_types = 6 ([[elektron]], [[neutrino elektron]], [[muon]], [[neutrino muon]], [[tau (partikel)|tau]], [[neutrino tau]]) |
||
| Baris 25: | Baris 25: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Special characters}} |
{{Special characters}} |
||
'''Lepton''' adalah sebuah kelompok [[partikel dasar]], bersama-sama dengan [[kuark]] dan [[ |
'''Lepton''' adalah sebuah kelompok [[partikel dasar]], bersama-sama dengan [[kuark]] dan [[gauge boson]]. |
||
Seperti kuark, lepton merupakan [[fermion]] (partikel spin {{frac|1|2}}) dan dipengaruhi oleh [[gaya elektromagnetik]], [[gaya gravitasi]], dan [[gaya lemah]], namun berbeda dengan kuark, lepton tidak ikut serta dalam [[interaksi kuat]]. |
Seperti kuark, lepton merupakan [[fermion]] (partikel spin {{frac|1|2}}) dan dipengaruhi oleh [[gaya elektromagnetik]], [[gaya gravitasi]], dan [[gaya lemah]], namun berbeda dengan kuark, lepton tidak ikut serta dalam [[interaksi kuat]]. |
||
| Baris 34: | Baris 34: | ||
== Pranala == |
== Pranala == |
||
*{{cite journal |
* {{cite journal |
||
|author=C. Amsler ''et al''. ([[Particle Data Group]]) |
|author=C. Amsler ''et al''. ([[Particle Data Group]]) |
||
|year=2008 |
|year=2008 |
||
| Baris 71: | Baris 71: | ||
|display-authors=29 |
|display-authors=29 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite journal |
* {{cite journal |
||
|author=I.V. Anicin |
|author=I.V. Anicin |
||
|year=2005 |
|year=2005 |
||
| Baris 79: | Baris 79: | ||
|bibcode = 2005physics...3172A |
|bibcode = 2005physics...3172A |
||
|pages=3172 }} |
|pages=3172 }} |
||
*{{cite journal |
* {{cite journal |
||
|author=Y.Fukuda ''et al''. |
|author=Y.Fukuda ''et al''. |
||
|year=1998 |
|year=1998 |
||
| Baris 149: | Baris 149: | ||
|bibcode = 1998PhRvL..81.1562F |display-authors=8 |
|bibcode = 1998PhRvL..81.1562F |display-authors=8 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite journal |
* {{cite journal |
||
|author=K. Kodama |
|author=K. Kodama |
||
|year=2001 |
|year=2001 |
||
| Baris 216: | Baris 216: | ||
|display-authors=29 |
|display-authors=29 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
|author=B.R. Martin, G. Shaw |
|author=B.R. Martin, G. Shaw |
||
|year=1992 |
|year=1992 |
||
|chapter=Chapter 2 – Leptons, quarks and hadrons |
|chapter=Chapter 2 – Leptons, quarks and hadrons |
||
|title=Particle Physics |
|title=Particle Physics |
||
|url=https://archive.org/details/particlephysics0000mart |
|||
|pages=23–47 |
|||
|pages=[https://archive.org/details/particlephysics0000mart/page/23 23]–47 |
|||
|publisher=[[John Wiley & Sons]] |
|publisher=[[John Wiley & Sons]] |
||
|isbn=0-471-92358-3 |
|isbn=0-471-92358-3 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite journal |
* {{cite journal |
||
|author=S.H. Neddermeyer, C.D. Anderson |
|author=S.H. Neddermeyer, C.D. Anderson |
||
|year=1937 |
|year=1937 |
||
| Baris 235: | Baris 236: | ||
|bibcode = 1937PhRv...51..884N |last2=Anderson |
|bibcode = 1937PhRv...51..884N |last2=Anderson |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite web |
* {{cite web |
||
|author=J. Peltoniemi, J. Sarkamo |
|author=J. Peltoniemi, J. Sarkamo |
||
|year=2005 |
|year=2005 |
||
| Baris 243: | Baris 244: | ||
|accessdate=2008-11-07 |
|accessdate=2008-11-07 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite journal |
* {{cite journal |
||
|author=M.L. Perl ''et al''. |
|author=M.L. Perl ''et al''. |
||
|year=1975 |
|year=1975 |
||
| Baris 310: | Baris 311: | ||
|display-authors=8 |
|display-authors=8 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
|author=M.E. Peskin, D.V. Schroeder |
|author=M.E. Peskin, D.V. Schroeder |
||
|title=Introduction to Quantum Field Theory |
|title=Introduction to Quantum Field Theory |
||
|url=https://archive.org/details/introductiontoqu0000pesk |
|||
|year=1995 |
|year=1995 |
||
|publisher=[[Westview Press]] |
|publisher=[[Westview Press]] |
||
|isbn=0-201-50397-2 |
|isbn=0-201-50397-2 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite journal |
* {{cite journal |
||
|author=K. Riesselmann |
|author=K. Riesselmann |
||
|year=2007 |
|year=2007 |
||
| Baris 325: | Baris 327: | ||
|volume=4 |issue=2 |
|volume=4 |issue=2 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
|author=L. Rosenfeld |
|author=L. Rosenfeld |
||
|year=1948 |
|year=1948 |
||
| Baris 332: | Baris 334: | ||
|publisher=[[Interscience Publishers]] |
|publisher=[[Interscience Publishers]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
|author=R. Shankar |
|author=R. Shankar |
||
|year=1994|edition=2nd |
|year=1994|edition=2nd |
||
|chapter=Chapter 2 – Rotational Invariance and Angular Momentum |
|chapter=Chapter 2 – Rotational Invariance and Angular Momentum |
||
|title=Principles of Quantum Mechanics |
|title=Principles of Quantum Mechanics |
||
|url=https://archive.org/details/principlesofquan0000shan_x3c9 |
|||
|pages=305–352 |
|||
|pages=[https://archive.org/details/principlesofquan0000shan_x3c9/page/305 305]–352 |
|||
|publisher=[[Springer (publisher)|Springer]] |
|publisher=[[Springer (publisher)|Springer]] |
||
|isbn=978-0-306-44790-7 |
|isbn=978-0-306-44790-7 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
|author=S. Weinberg |
|author=S. Weinberg |
||
|year=2003 |
|year=2003 |
||
|title=The Discovery of Subatomic Particles |
|title=The Discovery of Subatomic Particles |
||
|url=https://archive.org/details/discoveryofsubat00wein_0 |
|||
|publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]] |
|publisher=[[Cambridge University Press]] |
||
|isbn=0-521-82351-X |
|isbn=0-521-82351-X |
||
}} |
}} |
||
*{{cite book |
* {{cite book |
||
|author=R. Wilson |
|author=R. Wilson |
||
|year=1997 |
|year=1997 |
||
| Baris 360: | Baris 364: | ||
{{Commons category|Leptons}} |
{{Commons category|Leptons}} |
||
{{wiktionary|lepton}} |
{{wiktionary|lepton}} |
||
*[http://pdg.lbl.gov Particle Data Group homepage]. The PDG compiles authoritative information on particle properties. |
* [http://pdg.lbl.gov Particle Data Group homepage]. The PDG compiles authoritative information on particle properties. |
||
*[http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/particles/lepton.html Leptons], a summary of leptons from ''[[Hyperphysics]]''. |
* [http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/particles/lepton.html Leptons], a summary of leptons from ''[[Hyperphysics]]''. |
||
{{partikel}} |
{{partikel}} |
||
{{fisika-stub}} |
{{fisika-stub}} |
||
[[Kategori:Konsep |
[[Kategori:Konsep dalam fisika]] |
||
[[Kategori:Partikel subatom]] |
[[Kategori:Partikel subatom]] |
||
Revisi terkini sejak 19 Agustus 2024 13.21
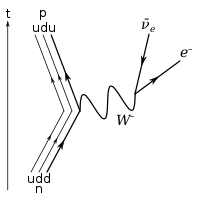 | |
| Komposisi: | Partikel dasar |
| Generasi: | 1, 2, 3 |
| Interaksi: | Elektromagnetik, Gravitasi, Interaksi lemah |
| Simbol: | l |
| Antipartikel: | Antilepton (l) |
| Tipe: | 6 (elektron, neutrino elektron, muon, neutrino muon, tau, neutrino tau) |
| Muatan listrik: | +1 e, 0 e, −1 e |
| Muatan warna: | Tidak ada |
| Spin: | ½ |
Lepton adalah sebuah kelompok partikel dasar, bersama-sama dengan kuark dan gauge boson.
Seperti kuark, lepton merupakan fermion (partikel spin ½) dan dipengaruhi oleh gaya elektromagnetik, gaya gravitasi, dan gaya lemah, namun berbeda dengan kuark, lepton tidak ikut serta dalam interaksi kuat.
Ada enam rasa lepton, yang membentuk tiga generasi. Generasi pertama adalah lepton elektronik, yang terdiri dari elektron dan neutrino elektron. Generasi kedua adalah lepton muon, terdiri dari muon dan neutrino muon, sedangkan generasi ketiga adalah tauon dan neutrino tauon. Tiap lepton memiliki antipartikel, yang dikenal sebagai antilepton.
Lepton adalah bagian penting dari Model standar, terutama elektron yang merupakan salah satu komponen atom, bersama-sama dengan proton dan neutron. Atom eksotik dengan muon dan tauon sebagai ganti elektron juga dapat disintesis.
Pranala
[sunting | sunting sumber]- C. Amsler et al. (Particle Data Group); Amsler; Doser; Antonelli; Asner; Babu; Baer; Band; Barnett; Bergren; Beringer; Bernardi; Bertl; Bichsel; Biebel; Bloch; Blucher; Blusk; Cahn; Carena; Caso; Ceccucci; Chakraborty; Chen; Chivukula; Cowan; Dahl; d'Ambrosio; Damour; et al. (2008). "Review of Particle Physics". Physics Letters B. 667: 1. Bibcode:2008PhLB..667....1P. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2008.07.018.
- I.V. Anicin (2005). "The Neutrino – Its Past, Present and Future". SFIN (Institute of Physics, Belgrade) year XV, Series A: Conferences, No. A2 (2002) 3–59: 3172. arXiv:physics/0503172
 . Bibcode:2005physics...3172A.
. Bibcode:2005physics...3172A. - Y.Fukuda; Hayakawa, T.; Ichihara, E.; Inoue, K.; Ishihara, K.; Ishino, H.; Itow, Y.; Kajita, T.; et al. (1998). "Evidence for Oscillation of Atmospheric Neutrinos". Physical Review Letters. 81 (8): 1562–1567. arXiv:hep-ex/9807003
 . Bibcode:1998PhRvL..81.1562F. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.1562.
. Bibcode:1998PhRvL..81.1562F. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.1562. - K. Kodama; Ushida, N.; Andreopoulos, C.; Saoulidou, N.; Tzanakos, G.; Yager, P.; Baller, B.; Boehnlein, D.; Freeman, W.; Lundberg, B.; Morfin, J.; Rameika, R.; Yun, J.C.; Song, J.S.; Yoon, C.S.; Chung, S.H.; Berghaus, P.; Kubantsev, M.; Reay, N.W.; Sidwell, R.; Stanton, N.; Yoshida, S.; Aoki, S.; Hara, T.; Rhee, J.T.; Ciampa, D.; Erickson, C.; Graham, M.; Heller, K.; et al. (2001). "Observation of tau neutrino interactions". Physics Letters B. 504 (3): 218. arXiv:hep-ex/0012035
 . Bibcode:2001PhLB..504..218D. doi:10.1016/S0370-2693(01)00307-0.
. Bibcode:2001PhLB..504..218D. doi:10.1016/S0370-2693(01)00307-0. - B.R. Martin, G. Shaw (1992). "Chapter 2 – Leptons, quarks and hadrons". Particle Physics. John Wiley & Sons. hlm. 23–47. ISBN 0-471-92358-3.
- S.H. Neddermeyer, C.D. Anderson; Anderson (1937). "Note on the Nature of Cosmic-Ray Particles". Physical Review. 51 (10): 884–886. Bibcode:1937PhRv...51..884N. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.51.884.
- J. Peltoniemi, J. Sarkamo (2005). "Laboratory measurements and limits for neutrino properties". The Ultimate Neutrino Page. Diakses tanggal 2008-11-07. Hapus pranala luar di parameter
|work=(bantuan) - M.L. Perl; Abrams, G.; Boyarski, A.; Breidenbach, M.; Briggs, D.; Bulos, F.; Chinowsky, W.; Dakin, J.; et al. (1975). "Evidence for Anomalous Lepton Production in e+–e− Annihilation". Physical Review Letters. 35 (22): 1489–1492. Bibcode:1975PhRvL..35.1489P. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.35.1489.
- M.E. Peskin, D.V. Schroeder (1995). Introduction to Quantum Field Theory. Westview Press. ISBN 0-201-50397-2.
- K. Riesselmann (2007). "Logbook: Neutrino Invention". Symmetry Magazine. 4 (2).
- L. Rosenfeld (1948). Nuclear Forces. Interscience Publishers. hlm. xvii.
- R. Shankar (1994). "Chapter 2 – Rotational Invariance and Angular Momentum". Principles of Quantum Mechanics (edisi ke-2nd). Springer. hlm. 305–352. ISBN 978-0-306-44790-7.
- S. Weinberg (2003). The Discovery of Subatomic Particles. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-82351-X.
- R. Wilson (1997). Astronomy Through the Ages: The Story of the Human Attempt to Understand the Universe. CRC Press. hlm. 138. ISBN 0-7484-0748-0.
Pranala luar
[sunting | sunting sumber]- Particle Data Group homepage. The PDG compiles authoritative information on particle properties.
- Leptons, a summary of leptons from Hyperphysics.
