Korteks orbitofrontal
| Korteks orbitofrontal | |
|---|---|
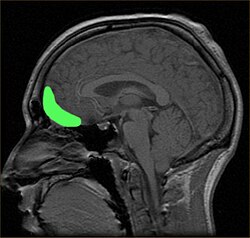 Perkiraan lokasi korteks orbitofrontal yang ditunjukkan pada MRI sagital | |
 Permukaan orbital dari lobus frontal kiri | |
| Rincian | |
| Bagian dari | Lobus frontal |
| Pengidentifikasi | |
| Bahasa Latin | cortex orbitofrontalis |
| NeuroNames | 91 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1049 |
| FMA | 242003 |
| Daftar istilah neuroanatomi | |
Korteks orbitofrontal adalah daerah korteks prefrontal di lobus frontal otak yang terlibat dalam proses kognitif pengambilan keputusan. Pada primata non-manusia, korteks ini terletak di area korteks asosiasi, yaitu area Brodmann 11, 12, dan 13. Sedangkan pada manusia, korteks ini terletak di area Brodmann 10, 11, dan 47.[1]
Korteks orbitofrontal secara fungsional terkait dengan korteks prefrontal ventromedial.[2] Oleh karena itu, area ini sangat istimewa karena koneksi saraf yang khas dan fungsi-fungsi yang unik.[3] Area ini merupakan bagian dari korteks prefrontal yang menerima proyeksi dari nukleus dorsal medial pada talamus, dan dianggap merepresentasikan emosi, rasa, penciuman, dan penghargaan dalam pengambilan keputusan.[4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11] Namanya diambil dari posisinya yang berada tepat di atas orbit tempat mata berada. Variabilitas yang cukup besar pada setiap individu telah ditemukan dalam Korteks orbitofrontal manusia.[12] Area yang serupa juga ditemukan pada hewan pengerat.[13]
Referensi
[sunting | sunting sumber]- ^ Kringelbach M. L. (2005). "The orbitofrontal cortex: linking reward to hedonic experience". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 6 (9): 691–702. doi:10.1038/nrn1747. PMID 16136173.
- ^ Phillips, LH., MacPherson, SE. & Della Sala, S. (2002). 'Age, cognition and emotion: the role of anatomical segregation in the frontal lobes: the role of anatomical segregation in the frontal lobes'. in J Grafman (ed.), Handbook of Neuropsychology: the frontal lobes. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp. 73-98.
- ^ Barbas H, Ghashghaei H, Rempel-Clower N, Xiao D (2002) Anatomic basis of functional specialization in prefrontal cortices in primates. In: Handbook of Neuropsychology (Grafman J, ed), pp 1-27. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science B.V.
- ^ Gottfried JA, Zald DH. On the scent of human olfactory orbitofrontal cortex: meta-analysis and comparison to non-human primates. Brain Res Rev 2005;50:287–304.
- ^ Rolls ET. The functions of the orbitofrontal cortex. Brain Cogn 2004;55:11–29.
- ^ Kringelbach ML. The human orbitofrontal cortex: linking reward to hedonic experience. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005;6:691–702
- ^ Rushworth M, Behrens T, Rudebeck P, Walton M. Contrasting roles for cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex in decisions and social behaviour. Trends Cogn Sci 2007;11: 168–176.
- ^ Dixon ML, Thiruchselvam R, Todd RM, ChristoffK. Emotion and the prefrontal cortex: an integrative review. Psychol Bull 2017;143:1033–1081.
- ^ Kringelbach ML, Rolls ET. The functional neuroanatomy of the human orbitofrontal cortex: evidence from neuroimaging and neuropsychology. Prog Neurobiol 2004;72: 341–372.
- ^ Damasio AR. Descartes’Error: Emotion, Reason and the Human Brain. New York: Putnam; 1994.
- ^ Fuster, J.M. The Prefrontal Cortex, (Raven Press, New York, 1997).
- ^ Isamah N, Faison W, Payne ME, MacFall J, Steffens DC, Beyer JL, Krishnan R, Taylor WD (2010). "Variability in Frontotemporal Brain Structure: The Importance of Recruitment of African Americans in Neuroscience Research". PLOS ONE. 5 (10): e13642. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...513642I. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013642
 . PMC 2964318
. PMC 2964318  . PMID 21049028.
. PMID 21049028.
- ^ Uylings HB, Groenewegen HJ, Kolb B (2003). "Do rats have a prefrontal cortex?". Behav Brain Res. 146 (1–2): 3–17. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2003.09.028. PMID 14643455.
Artikel ini tidak memiliki kategori atau memiliki terlalu sedikit kategori. Bantulah dengan menambahi kategori yang sesuai. Lihat artikel yang sejenis untuk menentukan apa kategori yang sesuai. Tolong bantu Wikipedia untuk menambahkan kategori. Tag ini diberikan pada Maret 2023. |
