Ukuran (matematika)
Artikel atau sebagian dari artikel ini mungkin diterjemahkan dari Measure (mathematics) di en.wiki-indonesia.club. Isinya masih belum akurat, karena bagian yang diterjemahkan masih perlu diperhalus dan disempurnakan. Jika Anda menguasai bahasa aslinya, harap pertimbangkan untuk menelusuri referensinya dan menyempurnakan terjemahan ini. Anda juga dapat ikut bergotong royong pada ProyekWiki Perbaikan Terjemahan. (Pesan ini dapat dihapus jika terjemahan dirasa sudah cukup tepat. Lihat pula: panduan penerjemahan artikel) |
Keseluruhan atau sebagian dari artikel ini membutuhkan perhatian dari ahli subyek terkait. Jika Anda adalah ahli yang dapat membantu, silakan membantu perbaiki kualitas artikel ini. |
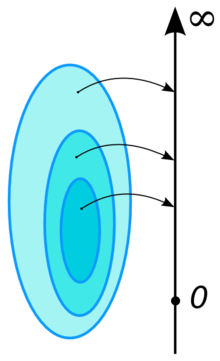
Dalam matematika, konsep ukuran umumnya merujuk pada pengertian seperti "panjang", "luas" dan "volume".
Teori ukuran adalah cabang analisis real yang menginvestigasi aljabar σ, ukuran, fungsi ukuran dan integral.
Referensi
- R. G. Bartle, 1995. The Elements of Integration and Lebesgue Measure. Wiley Interscience.
- Bourbaki, Nicolas (2004), Integration I, Springer Verlag, ISBN 3-540-41129-1 Chapter III.
- R. M. Dudley, 2002. Real Analysis and Probability. Cambridge University Press.
- Folland, Gerald B. (1999), Real Analysis: Modern Techniques and Their Applications, John Wiley and Sons, ISBN 0-471-317160-0 Periksa nilai: length
|isbn=(bantuan) Second edition. - D. H. Fremlin, 2000. Measure Theory. Torres Fremlin.
- Paul Halmos, 1950. Measure theory. Van Nostrand and Co.
- R. Duncan Luce and Louis Narens (1987). "measurement, theory of," The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics, v. 3, pp. 428-32.
- M. E. Munroe, 1953. Introduction to Measure and Integration. Addison Wesley.
- Shilov, G. E., and Gurevich, B. L., 1978. Integral, Measure, and Derivative: A Unified Approach, Richard A. Silverman, trans. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-63519-8. Emphasizes the Daniell integral.
