Neanderthal: Perbedaan antara revisi
→Budaya populer: menambah referensi. |
Tidak ada ringkasan suntingan |
||
| (3 revisi perantara oleh 3 pengguna tidak ditampilkan) | |||
| Baris 1: | Baris 1: | ||
{{Taxobox |
{{Taxobox |
||
| name = Neanderthal |
|||
| fossil_range = [[Pleistosen]] |
| fossil_range = [[Pleistosen]] |
||
| image = Neanderthalensis.jpg |
| image = Neanderthalensis.jpg |
||
| Baris 18: | Baris 19: | ||
| range_map_width = 220px |
| range_map_width = 220px |
||
| range_map_caption = Neanderthal range --> |
| range_map_caption = Neanderthal range --> |
||
| ⚫ | }}{{Linimasa manusia}}'''Neanderthal''' adalah anggota [[genus]] ''[[Homo (genus)|Homo]]'' yang telah punah dan berasal dari zaman [[Pleistosen]]. Spesimennya ditemukan di [[Eurasia]], dari [[Eropa Barat]] hingga [[Asia Tengah]] dan [[Asia Utara|Utara]]. Spesies ini dinamakan Neandertal sesuai dengan lokasi tempat pertama kali ditemukan di Jerman, Neandertal atau Lembah Neander. |
||
}} |
|||
| ⚫ | '''Neanderthal''' adalah anggota [[genus]] ''[[Homo (genus)|Homo]]'' yang telah punah dan berasal dari zaman [[Pleistosen]]. Spesimennya ditemukan di [[Eurasia]], dari [[Eropa Barat]] hingga [[Asia Tengah]] dan [[Asia Utara|Utara]]. Spesies ini dinamakan Neandertal sesuai dengan lokasi tempat pertama kali ditemukan di Jerman, Neandertal atau Lembah Neander. |
||
Neanderthal dapat diklasifikasikan sebagai subspesies manusia (''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis'') atau spesies yang berbeda (''Homo neanderthalensis'').<ref>{{cite journal |author=Tattersall I, Schwartz JH |title=Hominids and hybrids: the place of Neanderthals in human evolution |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=96 |issue=13 |pages=7117–9 |year=1999 |pmid=10377375 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7117 <!--Retrieved from CrossRef by DOI bot-->| quote =on the view that these distinctive hominids merit species recognition in their own right as '''Homo neanderthalensis''' (e.g., refs. 4 and 5), at least as many still regard them as no more than a strange variant of our own species, '''Homo sapiens''' (6, 7)}}. Tersedia [http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/96/13/7117 daring]</ref> Jejak proto-Neanderthal pertama muncul di Eropa 600.000–350.000 tahun yang lalu.<ref>{{cite journal | author = J. L. Bischoff et al. | year = 2003 | title = The Sima de los Huesos Hominids Date to Beyond U/Th Equilibrium (>350 kyr) and Perhaps to 400–500 kyr: New Radiometric Dates | journal = J. Archaeol. Sci. | issue = 30 | pages = 275 | volume = 30 | doi = 10.1006/jasc.2002.0834 <!--Retrieved from CrossRef by DOI bot-->}}</ref> |
Neanderthal dapat diklasifikasikan sebagai subspesies manusia (''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis'') atau spesies yang berbeda (''Homo neanderthalensis'').<ref>{{cite journal |author=Tattersall I, Schwartz JH |title=Hominids and hybrids: the place of Neanderthals in human evolution |journal=Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. |volume=96 |issue=13 |pages=7117–9 |year=1999 |pmid=10377375 | doi = 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7117 <!--Retrieved from CrossRef by DOI bot-->| quote =on the view that these distinctive hominids merit species recognition in their own right as '''Homo neanderthalensis''' (e.g., refs. 4 and 5), at least as many still regard them as no more than a strange variant of our own species, '''Homo sapiens''' (6, 7)}}. Tersedia [http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/96/13/7117 daring]</ref> Jejak proto-Neanderthal pertama muncul di Eropa 600.000–350.000 tahun yang lalu.<ref>{{cite journal | author = J. L. Bischoff et al. | year = 2003 | title = The Sima de los Huesos Hominids Date to Beyond U/Th Equilibrium (>350 kyr) and Perhaps to 400–500 kyr: New Radiometric Dates | journal = J. Archaeol. Sci. | issue = 30 | pages = 275 | volume = 30 | doi = 10.1006/jasc.2002.0834 <!--Retrieved from CrossRef by DOI bot-->}}</ref> |
||
| Baris 50: | Baris 50: | ||
== Budaya populer == |
== Budaya populer == |
||
[[Berkas:BlackTerror1636.jpg|jmpl|Manusia gua dalam ''The Black Terror #16'' (1946).]] |
|||
Neanderthal telah banyak muncul dalam budaya populer, antara lain dalam karya sastra, media visual, dan komedi. [[Arketipe]] "[[manusia gua]]" sering kali mengolok-olok Neanderthal dan menggambarkan mereka sebagai karakter primitif, bungkuk, menyeret buku-buku jari, menggunakan tongkat, mendengus, dan karakter [[asosial]] yang hanya dikendalikan oleh naluri binatang. "Neanderthal" juga digunakan sebagai kata hinaan.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Papagianni|first=Dimitra|last2=Morse|first2=M. A.|year=2015|url=https://books.google.co.id/books?id=9As7CwAAQBAJ&pg=PT171&redir_esc=y|title=The Neanderthals Rediscovered: How Modern Science Is Rewriting Their Story (The Rediscovered Series)|publisher=Thames & Hudson|isbn=978-0-500-77311-6|language=en|url-status=live}}</ref> |
Neanderthal telah banyak muncul dalam budaya populer, antara lain dalam karya sastra, media visual, dan komedi. [[Arketipe]] "[[manusia gua]]" sering kali mengolok-olok Neanderthal dan menggambarkan mereka sebagai karakter primitif, bungkuk, menyeret buku-buku jari, menggunakan tongkat, mendengus, dan karakter [[asosial]] yang hanya dikendalikan oleh naluri binatang. "Neanderthal" juga digunakan sebagai kata hinaan.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Papagianni|first=Dimitra|last2=Morse|first2=M. A.|year=2015|url=https://books.google.co.id/books?id=9As7CwAAQBAJ&pg=PT171&redir_esc=y|title=The Neanderthals Rediscovered: How Modern Science Is Rewriting Their Story (The Rediscovered Series)|publisher=Thames & Hudson|isbn=978-0-500-77311-6|language=en|url-status=live}}</ref> |
||
| Baris 55: | Baris 56: | ||
== Referensi == |
== Referensi == |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist/2}} |
||
== Pranala luar == |
== Pranala luar == |
||
Revisi terkini sejak 23 April 2024 00.23
| Neanderthal Rentang waktu: Pleistosen
| |
|---|---|
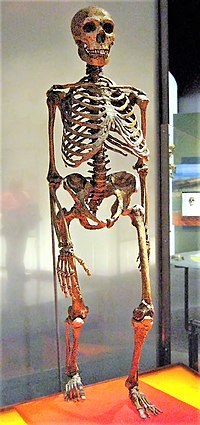
| |
| Kerangka Manusia Neanderthal, AMNH | |
| Klasifikasi ilmiah | |
| Kerajaan: | |
| Filum: | |
| Kelas: | |
| Ordo: | |
| Famili: | |
| Genus: | |
| Spesies: | H. neanderthalensis
|
| Nama binomial | |
| Homo neanderthalensis King, 1864
| |
| Sinonim | |
|
Palaeoanthropus neanderthalensis | |
−10 — – −9 — – −8 — – −7 — – −6 — – −5 — – −4 — – −3 — – −2 — – −1 — – 0 — |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Neanderthal adalah anggota genus Homo yang telah punah dan berasal dari zaman Pleistosen. Spesimennya ditemukan di Eurasia, dari Eropa Barat hingga Asia Tengah dan Utara. Spesies ini dinamakan Neandertal sesuai dengan lokasi tempat pertama kali ditemukan di Jerman, Neandertal atau Lembah Neander.
Neanderthal dapat diklasifikasikan sebagai subspesies manusia (Homo sapiens neanderthalensis) atau spesies yang berbeda (Homo neanderthalensis).[1] Jejak proto-Neanderthal pertama muncul di Eropa 600.000–350.000 tahun yang lalu.[2]
Pada situs-situs arkeologi Uluzzian (salah satu kelompok etnis dalam keluarga besar Neanderthal) di Italia Selatan telah ditemukan beragam peralatan hidup sehari-hari yang digunakan oleh Neanderthal.[3] Peralatan tersebut meliputi alat memancing, berburu, proyektil, serta peralatan lain dari tulang dan batu.[3] Hal ini menunjukkan bahwa Neanderthal mampu berinovasi dan membuat teknologi baru.[3]
Neanderthal berpisah dari garis evolusi manusia sekitar 500.000 tahun yang lalu dan lenyap dari muka bumi sekitar 30.000 tahun yang lalu.[3] Beberapa spekulasi yang diduga berkaitan dengan kepunahannya adalah Neanderthal mati dibunuh oleh manusia modern atau punah karena Homo sapiens lebih banyak dan aktif bereproduksi.[3] Spekulasi lainnya adalah tiga kali letusan gunung berapi sekitar 40.000 tahun yang lalu di daerah Italia dan Pegunungan Kaukasus telah menyebabkan kepunahan Nanderthal.[3]
Beberapa kumpulan artefak telah dikaitkan dengan Neanderthal di Eropa. Paling awal, alat batu Mousterian, diperkirakan dari 300.000 tahun yang lalu.[4] Artefak Mousterian terakhir ditemukan di Gua Gorham di pantai selatan Gibraltar.[5] Di luar Eropa, alat-alat Mousterian dibuat oleh Neanderthals dan Homo sapiens awal modern.[6]
Etimologi
[sunting | sunting sumber]Nama Neanderthal diambil dari nama Lembah Neandertal, di Jerman; tempat penemuan spesimen pertama yang teridentifikasi. Lembah tersebut dieja Neanderthal, sedangkan spesiesnya dieja Neanderthaler dalam bahasa Jerman hingga reformasi ejaan pada tahun 1901.[7][8]
Pengejaan Neandertal untuk spesies ini terkadang muncul dalam bahasa Inggris, bahkan dalam publikasi ilmiah. Namun, nama ilmiahnya, H. neanderthalensis, selalu dieja dengan th sesuai dengan prinsip prioritas. Umumnya, spesies ini selalu disebut Neandertaler dalam bahasa Jerman, yang berarti "penghuni Lembah Neander". Sementara, kata Neandertal selalu merujuk pada lembah.[8] Lembah itu sendiri namanya diambil dari Joachim Neander—seorang teolog dan penulis lagu-lagu pujian dari Jerman pada akhir abad ke-17—yang sering mengunjungi daerah tersebut.[9]
Neanderthal dapat diucapkan dengan menggunakan /t/ (seperti pada /niˈændərtɑːl/),[10] atau pelafalan bahasa Inggris standar th dengan frikatif /θ/ (seperti /niˈændərθɔːl/).[11][12]

Spesimen tipe Neanderthal 1, dikenal sebagai "kranium Neanderthal" atau "tengkorak Neanderthal" dalam literatur antropologi; sedangkan individu yang direkonstruksi berdasarkan tengkorak tersebut terkadang disebut "manusia Neanderthal".[13] Nama binomialnya ialah Homo neanderthalensis—yang memperluas nama "manusia Neanderthal" dari spesimen individu ke semua spesies, dan secara resmi mengakui bahwa spesies ini berbeda dengan manusia—pertama kali diusulkan oleh ahli geologi Irlandia bernama William King dalam sebuah makalah yang dibacakan di British Science Association ke-33 pada 1863.[14][15][16] Tahun berikutnya, pada 1864, ia mengusulkan agar Neanderthal dan manusia modern diklasifikasikan dalam genera yang berbeda setelah ia membandingkan tempurung otak Neanderthal dengan simpanse. Ia berargumen bahwa Neanderthal "tidak mampu memiliki konsepsi moral dan [teistik]".[17]
Budaya populer
[sunting | sunting sumber]
Neanderthal telah banyak muncul dalam budaya populer, antara lain dalam karya sastra, media visual, dan komedi. Arketipe "manusia gua" sering kali mengolok-olok Neanderthal dan menggambarkan mereka sebagai karakter primitif, bungkuk, menyeret buku-buku jari, menggunakan tongkat, mendengus, dan karakter asosial yang hanya dikendalikan oleh naluri binatang. "Neanderthal" juga digunakan sebagai kata hinaan.[18]
Pada karya sastra, mereka terkadang digambarkan sebagai sosok yang kejam atau mengerikan, seperti dalam novel The Grisly Folk karya H. G. Wells dan The Animal Wife karya Elizabeth Marshall Thomas. Selain itu, mereka juga digambarkan sebagai sosok yang beradab, tetapi memiliki budaya yang tidak lazim, seperti pada novel The Inheritors karya William Golding, Dance of the Tiger karya Björn Kurtén, serta Clan of the Cave Bear dan seri Earth's Children karya Jean M. Auel.[19]
Referensi
[sunting | sunting sumber]- ^ Tattersall I, Schwartz JH (1999). "Hominids and hybrids: the place of Neanderthals in human evolution". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (13): 7117–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.13.7117. PMID 10377375.
on the view that these distinctive hominids merit species recognition in their own right as Homo neanderthalensis (e.g., refs. 4 and 5), at least as many still regard them as no more than a strange variant of our own species, Homo sapiens (6, 7)
. Tersedia daring - ^ J. L. Bischoff; et al. (2003). "The Sima de los Huesos Hominids Date to Beyond U/Th Equilibrium (>350 kyr) and Perhaps to 400–500 kyr: New Radiometric Dates". J. Archaeol. Sci. 30 (30): 275. doi:10.1006/jasc.2002.0834.
- ^ a b c d e f Luki, Aulia (2021-01-19). "Antropologi: Neanderthal Juga "Manusia"". The New York Times/Discovery News/Science Daily. Kompas. hlm. 14.
- ^ Skinner, A., B. Blackwell, R. Long, M.R. Seronie-Vivien, A.-M. Tillier and J. Blickstein (2007-03-28). "New ESR dates for a new bone-bearing layer at Pradayrol, Lot, France". Paleoanthropology Society.
- ^ Finlayson, C; Pacheco, Fg; Rodríguez-Vidal, J; Fa, Da; Gutierrez, López, Jm; Santiago, Pérez, A; Finlayson, G; Allue, E; Baena, Preysler, J; Cáceres, I; Carrión, Js; Fernández, Jalvo, Y; Gleed-Owen, Cp; Jimenez, Espejo, Fj; López, P; López, Sáez, Ja; Riquelme, Cantal, Ja; Sánchez, Marco, A; Guzman, Fg; Brown, K; Fuentes, N; Valarino, Ca; Villalpando, A; Stringer, Cb; Martinez, Ruiz, F; Sakamoto, T (October 2006). "Late survival of Neanderthals at the southernmost extreme of Europe". Nature. 443 (7113): 850–3. Bibcode:2006Natur.443..850F. doi:10.1038/nature05195. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 16971951.
- ^ Donald Johanson & Blake Edgar (2006). "From Lucy to Language". Simon & Schuster: 272.
- ^ Howell, F. C. (1957). "The Evolutionary Significance of Variation and Varieties of "Neanderthal" Man". The Quarterly Review of Biology. 32 (4): 330–347. doi:10.1086/401978. ISSN 0033-5770.
- ^ a b "Neandertal oder Neanderthal? - Was ist denn nun richtig?" [Neandertal atau Neanderthal? - Mana yang benar?]. mettmann.de. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal 3 Oktober 2006. Diakses tanggal 22 Januari 2023.
- ^ Schmitz, Ralf W.; dkk. (2002). "The Neandertal type site revisited: Interdisciplinary investigations of skeletal remains from the Neander Valley, Germany". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (dalam bahasa Inggris). 99 (20): 13342–13347. doi:10.1073/pnas.192464099. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 130635
 . PMID 12232049.
. PMID 12232049.
- ^ "Neanderthal". Collins English Dictionary. Diakses tanggal 25 Januari 2023.
- ^ "Neanderthal". Merriam-Webster Dictionary (dalam bahasa Inggris). Diakses tanggal 25 Januari 2023.
- ^ "Neanderthal". American Heritage Dictionary. Diakses tanggal 25 Januari 2023.
- ^ Vogt, K. C.; Hunt, James (1864). Lectures on man; his place in creation, and in the history of the earth. London, Longman, Green, Longman, and Roberts. hlm. 302, 473.
- ^ King, W. (1864). "On the Neanderthal skull, or reasons for believing it to belong to the Clydian Period and to a species different from that represented by man". Report of the British Association for the Advancement of Science, Notices and Abstracts, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, 1863. 33: 81–82 – via Biodiversity Heritage Library.
- ^ Murray, John; dkk. (2015). "The Contribution of William King to the Early Development of Palaeoanthropology". Irish Journal of Earth Sciences. 33: 1–16. doi:10.3318/ijes.2015.33.1. ISSN 0790-1763.
- ^ Winner, A. K. (1964). "Terminology". Current Anthropology (dalam bahasa Inggris). 5 (2): 119–122. doi:10.1086/200469. ISSN 0011-3204.
- ^ King, W. (1864). "The reputed fossil man of the Neanderthal" (PDF). Quarterly Journal of Science. 1: 96.
- ^ Papagianni, Dimitra; Morse, M. A. (2015). The Neanderthals Rediscovered: How Modern Science Is Rewriting Their Story (The Rediscovered Series) (dalam bahasa Inggris). Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-77311-6.
- ^ Drell, J. R. R. (2000). "Neanderthals: A History of Interpretation". Oxford Journal of Archaeology (dalam bahasa Inggris). 19 (1): 1–24. doi:10.1111/1468-0092.00096. ISSN 0262-5253.
Pranala luar
[sunting | sunting sumber]- Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
- Smithsonian Diarsipkan 11 September 2007 di Wayback Machine.
- Archaelogy Info Diarsipkan 26 Desember 2018 di Wayback Machine.
- MNSU Diarsipkan 23 Oktober 2010 di Wayback Machine.
- "Humans and Neanderthals interbred" Diarsipkan 22 Februari 2009 di Wayback Machine.: Modern humans contain a little bit of Neanderthal, according to a new theory, because the two interbred and became one species. (Cosmos magazine, November 2006)
- BBC.co.uk - 'Neanderthals "mated with modern humans": A hybrid skeleton showing features of both Neanderthal and early modern humans has been discovered, challenging the theory that our ancestors drove Neanderthals to extinction', BBC (21 April 1999)
- BBC.co.uk - 'Neanderthals "had hands like ours": The popular image of Neanderthals as clumsy, backward creatures has been dealt another blow', Helen Briggs, BBC (27 Maret 2003)
- IndState.edu Diarsipkan 3 Maret 2001 di Wayback Machine. - 'Neanderthals: A Cyber Perspective', Kharlena María Ramanan, Indiana State University (1997)
- Krapina.com - 'Krapina: The World's Largest Neanderthal Finding Site'
- Neanderthal.de - 'Neanderthal Museum'
- Neanderthal DNA - 'Neanderthal DNA' Includes Neanderthal mtDNA sequences
- The Cryptid Zoo - 'Neanderthals and Neanderthaloids in Cryptozoology' (modern sightings promoted by the pseudoscience of cryptozoology)
- UniZH.ch Diarsipkan 13 Mei 2007 di Wayback Machine. - 'Comparing Neanderthals and modern humans: Neanderthals differ from anatomically modern Homo sapiens in a suite of cranial features' (cranio-facial reconstructions), Institut für Informatik der Universität Zürich
- Panoramio Diarsipkan 24 Juli 2018 di Wayback Machine. - 'IMG_6922 The Neandertal foot prints' (photo of ~25K years old fossilized footprints discovered in 1970 on volcanic layers near Demirkopru Dam Reservoir, Manisa, Turkey)
- interactive database on the archaeology and anthropology of Neanderthals Diarsipkan 29 September 2007 di Wayback Machine.
- Did free trade cause the extinction of Neanderthals?
- Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA can show conflicting phylogenetic histories
- Neanderthal manifactured pitch Diarsipkan 23 Mei 2008 di Wayback Machine.
- Homo neanderthalensis reconstruction Diarsipkan 26 September 2006 di Wayback Machine. - Electronic articles published by the Division of Anthropology, American Museum of Natural History.
- CBS article on latest scientific speculation about Neanderthals in Gibraltar.
- Neanderthal bone gives DNA clues
- Scientists decode Neanderthal genes
- Scientists Build 'Frankenstein' Neanderthal Skeleton
- A NEANDERTHAL'S DNA TALE Diarsipkan 6 Maret 2008 di Wayback Machine.
- 'Bone and Stone' A digitally enhanced single frame philatelic exhibit dedicated to the Neanderthal.
- How Neanderthal molar teeth grew
- Mousterian Tools of Neanderthals From Europe - World Museum of Man Diarsipkan 3 Februari 2010 di Wayback Machine.
- The Way We Are
- Link to picture of the Neanderthal trace near Gediz River in Turkey Diarsipkan 24 Juli 2018 di Wayback Machine.
- Link to Cross-Eyed stereoview of Neanderthal fossil cast in Chicago Field Museum Diarsipkan 24 Februari 2009 di Wayback Machine.
- (Indonesia) Homo sapiens Mendesak Homo neanderthalensis Keluar dari Eropa
