Pembicaraan Pengguna:Kucing gelap
- Bacalah halaman Pengantar Wikipedia terlebih dahulu.
- Baca juga informasi tentang berkontribusi di Wikipedia.
- Lihat pula aturan yang disederhanakan sebelum melanjutkan.
- Selalu tanda tangani pertanyaan Anda di Warung Kopi atau halaman pembicaraan dengan mengetikkan
~~~~pada akhir kalimat Anda. - Jangan takut! Anda tidak perlu takut salah ketika menyunting atau membuat halaman baru, menambahkan, atau menghapus kalimat.
Selamat menjelajah, kami menunggu suntingan Anda di Wikipedia bahasa Indonesia!
Welcome! If you do not understand Indonesian language, you may want to visit the embassy or find users who speak your language. Enjoy!
Undangan ProyekWiki Bahasa

|
Halo kami mengundang Anda untuk bergabung dan berpartisipasi di dalam ProyekWiki Bahasa
|
NyıLVoskT • ~~~ 23 Maret 2023 09.39 (UTC)
Rumpun bahasa Algik
Rumpun bahasa Algik
Algonquian–Ritwan Algonquian–Wiyot–Yurok | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persebaran | Bagian utara benua Amerika Utara | ||||
| |||||
| Bahasa induk | Proto-Algik | ||||
| Kode bahasa | |||||
| ISO 639-5 | aql | ||||
| Glottolog | algi1248 | ||||
| Lokasi penuturan | |||||
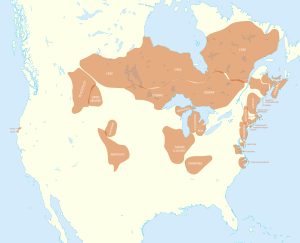 Distribusi pra-kontak bahasa Algik | |||||
| Catatan | |||||
| Tanda † menandakan bahwa bahasa itu telah punah | |||||
Rumpun bahasa Algik (yang juga dikenal sebagai Algonquian–Wiyot–Yurok atau Algonquian–Ritwan)[1][2] adalah rumpun bahasa asli yang berasal dari benua Amerika Utara. Sebagian Algonquian subfamily, dispersed over a broad area from the Rocky Mountains to Atlantic Canada. The other Algic languages are the Yurok and Wiyot of northwestern California, which, despite their geographic proximity, are not closely related. All these languages descend from Proto-Algic, a second-order proto-language estimated to have been spoken about 7,000 years ago and reconstructed using the reconstructed Proto-Algonquian language and the Wiyot and Yurok languages.
Bahasa Algic (juga Algonquian–Wiyot–Yurok atau Algonquian–Ritwan)[1][2] adalah rumpun bahasa asli Amerika Utara. Sebagian besar bahasa Algi termasuk dalam subfamili Algonquian, tersebar di wilayah yang luas dari Pegunungan Rocky hingga Atlantik Kanada. Bahasa Algic lainnya adalah Yurok dan Wiyot di barat laut California, yang meskipun letak geografisnya berdekatan, namun tidak berkerabat dekat. Semua bahasa ini diturunkan dari Proto-Algic, bahasa proto orde kedua yang diperkirakan telah diucapkan sekitar 7.000 tahun yang lalu dan direkonstruksi menggunakan bahasa Proto-Algonquian yang direkonstruksi serta bahasa Wiyot dan Yurok.

History
The term Algic was first coined by Henry Schoolcraft in his Algic Researches, published in 1839. Schoolcraft defined the term as "derived from the words Allegheny and Atlantic, in reference to the indigenous people anciently located in this geographical area."[3] Schoolcraft's terminology was not retained. The peoples he called "Algic" were later included among the speakers of Algonquian languages. This language group is also referred to as "Algonquian-Ritwan" and "Wiyot-Yurok-Algonquian."
When Edward Sapir proposed that the well-established Algonquian family was genetically related to the Wiyot and Yurok languages of northern California, he applied the term Algic to this larger family. The Algic urheimat is thought to have been located in the Northwestern United States somewhere between the suspected homeland of the Algonquian branch (to the west of Lake Superior according to Goddard[4]) and the earliest known location of the Wiyot and Yurok (along the middle Columbia River according to Whistler[5]).
Classification of Algic
The genetic relation of Wiyot and Yurok to Algonquian was first proposed by Edward Sapir (1913, 1915, 1923), and argued against by Algonquianist Truman Michelson (1914, 1914, 1935). According to Lyle Campbell (1997), the relationship "has subsequently been demonstrated to the satisfaction of all."[6] This controversy in the early classification of North American languages was called the "Ritwan controversy" because Wiyot and Yurok were assigned to a genetic grouping called "Ritwan." Most specialists now reject the validity of the Ritwan genetic node.[7] Berman (1982) suggested that Wiyot and Yurok share sound changes not shared by the rest of Algic (which would be explainable by either areal diffusion or genetic relatedness); Proulx (2004) argued against Berman's conclusion of common sound changes.[1]
More recently, Sergei Nikolaev has argued in two papers for a systematic relationship between the Nivkh language of Sakhalin and the Amur river basin and the Algic languages, and a secondary relationship between these two together and the Wakashan languages.[8][9]
Proto-language
See also
References
- ^ a b Berman, Howard (July 1984). "Proto-Algonquian-Ritwan Verbal Roots". International Journal of American Linguistics. 50 (3): 335–342. doi:10.1086/465840. ISSN 0020-7071.
- ^ Golla, Victor (20 September 2011). California Indian languages. Berkeley. hlm. 61. ISBN 9780520949522. OCLC 755008853.
- ^ Schoolcraft 1839
- ^ Goddard 1994
- ^ Moratto 1984
- ^ Campbell 2000, hlm. 152, who cites among others Haas 1958
- ^ Campbell 2000, hlm. 152; Mithun 1999, hlm. 337
- ^ Nikolaev 2015.
- ^ Nikolaev 2016.
Bibliography
Journals and books
- Berman, Howard (1982). "Two Phonological Innovations in Ritwan". International Journal of American Linguistics. 48 (4): 412–420. doi:10.1086/465750. ISSN 0020-7071.
- Campbell, Lyle (21 September 2000) [1997]. American Indian Languages: The Historical Linguistics of Native America (dalam bahasa Inggris). New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-509427-5.
- Goddard, Ives (1994). Cowan, William, ed. "The West-to-East cline in Algonquian dialectology". Actes du Vingt-cinquième Congrès des Algonquinistes. 25. hdl:10088/21761. Diakses tanggal 1 December 2018.
- Goddard, Ives (1996). "Languages". Dalam Sturtevant, W. C. Handbook of North American Indians. 17. Washington, D. C.: Smithsonian Institution. ISBN 978-0-16-048774-3.
- Haas, Mary R. (1958). "Algonkian-Ritwan: The End of a Controversy". International Journal of American Linguistics. 24 (3): 159–173. doi:10.1086/464453. ISSN 0020-7071.
- Haas, Mary R. (1966). "Wiyot-Yurok-Algonkian and Problems of Comparative Algonkian". International Journal of American Linguistics. 32 (2): 101–107. doi:10.1086/464889. ISSN 0020-7071.
- Michelson, Truman (1914). "Two Alleged Algonquian Languages of California". American Anthropologist. 16 (2): 361–367. doi:10.1525/aa.1914.16.2.02a00150. ISSN 0002-7294.
- Michelson, Truman. 1915. Rejoinder. American Anthropologist, n.s. 17:194–198.
- Michelson, Truman (1935). "Phonetic Shifts in Algonquian Languages". International Journal of American Linguistics. 8 (3/4): 131–171. doi:10.1086/463813. ISSN 0020-7071.
- Mithun, Marianne (1999). The languages of Native North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-23228-9. (hbk); ISBN 0-521-29875-X.
- Moratto, Michael J. (1984). California archaeology
 . Academic Press. ISBN 9780125061803.
. Academic Press. ISBN 9780125061803. - Nikolaev, Sergei L. (2015). "Toward the reconstruction of Proto-Algonquian-Wakashan. Part 1: Proof of the Algonquian-Wakashan relationship". Journal of Language Relationship (dalam bahasa Inggris). 13 (1): 23–61. doi:10.31826/jlr-2015-131-206
 . Diakses tanggal 1 December 2018.
. Diakses tanggal 1 December 2018. - Nikolaev, Sergei L. (2016). "Toward the reconstruction of Proto-Algonquian-Wakashan. Part 2: Algonquian-Wakashan sound correspondences". Journal of Language Relationship (dalam bahasa Inggris). 13 (4): 289–328. doi:10.31826/jlr-2016-133-408
 . Diakses tanggal 1 December 2018.
. Diakses tanggal 1 December 2018. - Proulx, Paul (1982). "Yurok Retroflection and Vowel Symbolism in Proto-Algic". Kansas Working Papers in Linguistics. 7: 119–123. doi:10.17161/KWPL.1808.3621
 . hdl:1808/3621. ISSN 1043-3805.
. hdl:1808/3621. ISSN 1043-3805. - Proulx, Paul (1984). "Proto-Algic I: Phonological Sketch". International Journal of American Linguistics. 50 (2): 165–207. doi:10.1086/465826. ISSN 0020-7071.
- Proulx, Paul (1985). "Proto-Algic II: Verbs". International Journal of American Linguistics. 51 (1): 59–93. doi:10.1086/465860. ISSN 0020-7071.
- Proulx, Paul (1991). "Proto-Algic III: Pronouns". Kansas Working Papers in Linguistics. 16: 129–170. doi:10.17161/KWPL.1808.429
 . hdl:1808/429. ISSN 1043-3805.
. hdl:1808/429. ISSN 1043-3805. - Proulx, Paul (1992). "Proto-Algic IV: Nouns". Kansas Working Papers in Linguistics. 17: 11–57. doi:10.17161/KWPL.1808.644
 . hdl:1808/644. ISSN 1043-3805.
. hdl:1808/644. ISSN 1043-3805. - Proulx, Paul (1994). "Proto-Algic V: Doublets and their Implications". Kansas Working Papers in Linguistics. 19 (2): 115–182. doi:10.17161/KWPL.1808.321
 . hdl:1808/321. ISSN 1043-3805.
. hdl:1808/321. ISSN 1043-3805. - Proulx, Paul (2004). "Proto Algic VI: Conditioned Yurok Reflexes of Proto Algic Vowels". Kansas Working Papers in Linguistics. 27: 124–138. doi:10.17161/KWPL.1808.1247
 . hdl:1808/1247. ISSN 1043-3805.
. hdl:1808/1247. ISSN 1043-3805. - Sturtevant, William C., ed. (1978). Handbook of North American Indians. 1–20. Washington, D. C.: Smithsonian Institution.
- Sapir, Edward (1913). "Wiyot and Yurok, Algonkin languages of California". American Anthropologist. 15 (4): 617–646. doi:10.1525/aa.1913.15.4.02a00040
 . ISSN 0002-7294.
. ISSN 0002-7294. - Sapir, E. (1922). "Algonkin languages of California: A reply". American Anthropologist. 17 (1): 188–198. doi:10.1525/aa.1915.17.1.02a00270
 . ISSN 0002-7294.
. ISSN 0002-7294. - Sapir, Edward (1922). "The Algonkin affinity of Yurok and Wiyot kinship terms". Journal de la Société des Américanistes. 14 (1): 36–74. doi:10.3406/jsa.1922.3991. hdl:1974/11913
 . ISSN 0037-9174.
. ISSN 0037-9174. - Schoolcraft, Henry Rowe (1839). Algic researches, comprising inquiries respecting the mental characteristics of the North American Indians. First series. Indian tales and legends. 1. New York: Harper & Brothers. OCLC 6836253. OL 17492450M.
Templat:Algic languages Templat:Language families Templat:North American languages Kucing gelap (bicara) 23 Maret 2023 21.20 (UTC)


