Barisan: Perbedaan antara revisi
Tampilan
Konten dihapus Konten ditambahkan
JohnThorne (bicara | kontrib) ←Membuat halaman berisi '<!--{{Redirect|Sequential|the manual transmission|Sequential manual transmission|other uses|Sequence (disambiguation)}}--> '''Urutan''' ({{lang-en|sequence}}) dalam...' |
JohnThorne (bicara | kontrib) Tidak ada ringkasan suntingan |
||
| Baris 1: | Baris 1: | ||
<!--{{Redirect|Sequential|the manual transmission|Sequential manual transmission|other uses|Sequence (disambiguation)}}--> |
<!--{{Redirect|Sequential|the manual transmission|Sequential manual transmission|other uses|Sequence (disambiguation)}}--> |
||
'''Urutan''' ({{lang-en|sequence}}) dalam [[matematika]], adalah suatu daftar tertata. Sebagaimana suatu [[himpunan]], urutan memuat [[Elemen (matematika)|anggota (juga disebut ''elemen'' atau ''term'')]]. Jumlah elemen tertata (kemungkinan tak terhingga) disebut ''panjang'' urutan. Berbeda dengan himpunan, penataan urutan sangat penting dan elemen-elemen yang tepat sama dapat muncul berulang kali pada posisi berbeda dalam urutan itu. Lebih tepatnya, suatu urutan dapat didefinisikan sebagai suatu [[fungsi (matematika)|fungsi]] di mana ranah (atau domain) darinya merupakan suatu himpunan [[countable]] [[totally ordered]], sepertu [[bilangan asli]]. |
|||
<!-- |
<!-- |
||
Misalnya, (M, A, R, Y) adalah suatu urutan huruf-huruf dengan is huruf 'M' pada posisi pertama dan 'Y' pada posisi terakhir. Urutan ini berbeda dengan (A, R, M, Y). Juga, urutan (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8), yang memuat angka 1 pada dua posisi berbeda, merupakan urutan yang valid. Urutan dapat bersifat ''[[:en:finite set|finite]]'', seperti pada contoh ini, atau ''[[:en:Infinite set|infinite]]'', seperti urutan semua [[integer]] [[:en:even and odd numbers|genap]] [[:en:positive and negative numbers|positif]] (2, 4, 6,...). Urutan finit kadangkala dikenal sebagai ''string'' atau ''word'' dan urutan infinit disebut juga ''stream''. Urutan yang kosong ( ) dimasukkan dalam kebanyakan pengertian urutan, tetapi dapat pula tidak dimasukkan tergantung dari konteksnya. |
|||
[[Image:Cauchy sequence illustration2.svg|right|thumb|350px| |
[[Image:Cauchy sequence illustration2.svg|right|thumb|350px|Suatu urutan infinit [[bilangan real]] (biru). Urutan ini tidak meningkat maupun menurut, maupun konvergen, maupun bersifat [[:en:Cauchy sequence|Cauchy]]. Namun, bersifat ''bounded''.]] |
||
<!-- |
|||
== |
== Contoh dan notasi == |
||
A sequence can be thought of as a list of elements with a particular order. Sequences are useful in a number of mathematical disciplines for studying [[Function (mathematics)|functions]], [[Space (mathematics)|spaces]], and other mathematical structures using the [[#Limits and convergence|convergence]] properties of sequences. In particular, sequences are the basis for [[series (mathematics)|series]], which are important in [[differential equations]] and [[analysis (mathematics)|analysis]]. Sequences are also of interest in their own right and can be studied as patterns or puzzles, such as in the study of [[prime number]]s. |
A sequence can be thought of as a list of elements with a particular order. Sequences are useful in a number of mathematical disciplines for studying [[Function (mathematics)|functions]], [[Space (mathematics)|spaces]], and other mathematical structures using the [[#Limits and convergence|convergence]] properties of sequences. In particular, sequences are the basis for [[series (mathematics)|series]], which are important in [[differential equations]] and [[analysis (mathematics)|analysis]]. Sequences are also of interest in their own right and can be studied as patterns or puzzles, such as in the study of [[prime number]]s. |
||
There are a number of ways to denote a sequence, some of which are more useful for specific types of sequences. One way to specify a sequence is to list the elements. For example, the first four odd numbers form the sequence (1,3,5,7). This notation can be used for infinite sequences as well. For instance, the infinite sequence of positive odd integers can be written (1,3,5,7,...). Listing is most useful for infinite sequences with a [[pattern]] that can be easily discerned from the first few elements. Other ways to denote a sequence are discussed after the examples. |
There are a number of ways to denote a sequence, some of which are more useful for specific types of sequences. One way to specify a sequence is to list the elements. For example, the first four odd numbers form the sequence (1,3,5,7). This notation can be used for infinite sequences as well. For instance, the infinite sequence of positive odd integers can be written (1,3,5,7,...). Listing is most useful for infinite sequences with a [[pattern]] that can be easily discerned from the first few elements. Other ways to denote a sequence are discussed after the examples. |
||
=== Contoh-contoh penting === |
|||
===Important examples=== |
|||
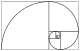
[[File:FibonacciBlocks.svg|thumb|220px|right|A tiling with squares whose sides are successive Fibonacci numbers in length.]] |
[[File:FibonacciBlocks.svg|thumb|220px|right|A tiling with squares whose sides are successive Fibonacci numbers in length.]] |
||
Revisi per 15 Desember 2014 20.48
Urutan (bahasa Inggris: sequence) dalam matematika, adalah suatu daftar tertata. Sebagaimana suatu himpunan, urutan memuat anggota (juga disebut elemen atau term). Jumlah elemen tertata (kemungkinan tak terhingga) disebut panjang urutan. Berbeda dengan himpunan, penataan urutan sangat penting dan elemen-elemen yang tepat sama dapat muncul berulang kali pada posisi berbeda dalam urutan itu. Lebih tepatnya, suatu urutan dapat didefinisikan sebagai suatu fungsi di mana ranah (atau domain) darinya merupakan suatu himpunan countable totally ordered, sepertu bilangan asli.
Jenis
- ±1-sequence
- Arithmetic progression
- Cauchy sequence
- Farey sequence
- Fibonacci sequence
- Geometric progression
- Look-and-say sequence
- Thue–Morse sequence
Konsep terkait
Operasi
Lihat pula
- Net (topology) (a generalization of sequences)
- On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences
- Permutation
- Recurrence relation
- Sequence space
- Set (mathematics)
Referensi
Pranala luar
 Definisi kamus barisan di Wikikamus
Definisi kamus barisan di Wikikamus- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001) [1994], "Sequence", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer Science+Business Media B.V. / Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences
- Journal of Integer Sequences (free)
- Sequence, PlanetMath.org.