Infeksi oportunistik: Perbedaan antara revisi
Tidak ada ringkasan suntingan |
Mengembangkan artikel |
||
| Baris 5: | Baris 5: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Infeksi oportunistik''' adalah [[infeksi]] yang disebabkan oleh organisme (seperti bakteri, jamur, parasit, atau virus) yang memanfaatkan kesempatan yang biasanya tidak tersedia. Kesempatan ini dapat berupa [[Imunodefisiensi|sistem imun yang melemah]] (misalnya akibat [[AIDS]] atau pemberian [[obat imunosupresif]], seperti pada [[perawatan kanker]]),<ref name=":1">{{cite book|vauthors=Justiz Vaillant AA, Qurie A|date=2021|title=StatPearls|place=Treasure Island (FL)|publisher=StatPearls Publishing|chapter=Immunodeficiency|pmid=29763203|access-date=9 Maret 2021|chapter-url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500027/|url-status=live}}</ref> perubahan [[mikrobioma]] (seperti gangguan pada [[mikrobiota usus]]), atau kerusakan pada [[sistem integumen]] (seperti pada [[trauma tajam]]). Banyak di antara organisme-organisme ini yang tidak menyebabkan penyakit pada inang sehat dengan sistem imun yang baik, dan dalam beberapa kasus, mereka berperan sebagai [[Komensalisme|komensal]] sampai keseimbangan sistem imun terganggu.<ref name=":2">{{cite journal|date=2016|title=Macrolide Resistance in ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''|journal=Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology|volume=6|pages=98|doi=10.3389/fcimb.2016.00098|pmc=5030221|pmid=27709102|vauthors=Schroeder MR, Stephens DS|doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|date=2014|title=Propionibacterium acnes: from commensal to opportunistic biofilm-associated implant pathogen|journal=Clinical Microbiology Reviews|volume=27|issue=3|pages=419–40|doi=10.1128/CMR.00092-13|pmc=4135900|pmid=24982315|vauthors=Achermann Y, Goldstein EJ, Coenye T, Shirtliff ME}}</ref> Suatu infeksi juga dapat disebut oportunistik jika suatu patogen menyebabkan penyakit ringan pada orang sehat, tetapi menyebabkan penyakit yang lebih serius saat kondisi tubuh inangnya memungkinkan.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Caballero|first=Mauricio T.|last2=Polack|first2=Fernando P.|date=2018|title=Respiratory syncytial virus is an “opportunistic” killer|url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ppul.23963|journal=Pediatric Pulmonology|volume=53|issue=5|pages=664–667|doi=10.1002/ppul.23963}}</ref> |
'''Infeksi oportunistik''' adalah [[infeksi]] yang disebabkan oleh organisme (seperti bakteri, jamur, parasit, atau virus) yang memanfaatkan kesempatan yang biasanya tidak tersedia. Kesempatan ini dapat berupa [[Imunodefisiensi|sistem imun yang melemah]] (misalnya akibat [[AIDS]] atau pemberian [[obat imunosupresif]], seperti pada [[perawatan kanker]]),<ref name=":1">{{cite book|vauthors=Justiz Vaillant AA, Qurie A|date=2021|title=StatPearls|place=Treasure Island (FL)|publisher=StatPearls Publishing|chapter=Immunodeficiency|pmid=29763203|access-date=9 Maret 2021|chapter-url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK500027/|url-status=live}}</ref> perubahan [[mikrobioma]] (seperti gangguan pada [[mikrobiota usus]]), atau kerusakan pada [[sistem integumen]] (seperti pada [[trauma tajam]]). Banyak di antara organisme-organisme ini yang tidak menyebabkan penyakit pada inang sehat dengan sistem imun yang baik, dan dalam beberapa kasus, mereka berperan sebagai [[Komensalisme|komensal]] sampai keseimbangan sistem imun terganggu.<ref name=":2">{{cite journal|date=2016|title=Macrolide Resistance in ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''|journal=Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology|volume=6|pages=98|doi=10.3389/fcimb.2016.00098|pmc=5030221|pmid=27709102|vauthors=Schroeder MR, Stephens DS|doi-access=free}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|date=2014|title=Propionibacterium acnes: from commensal to opportunistic biofilm-associated implant pathogen|journal=Clinical Microbiology Reviews|volume=27|issue=3|pages=419–40|doi=10.1128/CMR.00092-13|pmc=4135900|pmid=24982315|vauthors=Achermann Y, Goldstein EJ, Coenye T, Shirtliff ME}}</ref> Suatu infeksi juga dapat disebut oportunistik jika suatu patogen menyebabkan penyakit ringan pada orang sehat, tetapi menyebabkan penyakit yang lebih serius saat kondisi tubuh inangnya memungkinkan.<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Caballero|first=Mauricio T.|last2=Polack|first2=Fernando P.|date=2018|title=Respiratory syncytial virus is an “opportunistic” killer|url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ppul.23963|journal=Pediatric Pulmonology|volume=53|issue=5|pages=664–667|doi=10.1002/ppul.23963}}</ref> |
||
== Organisme oportunistik == |
|||
Berbagai macam patogen terlibat dalam infeksi oportunistik dan dapat menyebabkan berbagai kondisi patologis. Berikut ini beberapa patogen oportunistik dan kondisi yang ditimbulkannya. |
|||
=== Bakteri === |
|||
* ''[[Clostridioides difficile]]'' (dulu dikenal sebagai ''Clostridium difficile'') adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan infeksi pencernaan dan umumnya diasosiasikan dengan [[infeksi nosokomial]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Czepiel J, Dróżdż M, Pituch H, Kuijper EJ, Perucki W, Mielimonka A, Goldman S, Wultańska D, Garlicki A, Biesiada G | display-authors = 6 | title = Clostridium difficile infection: review | journal = European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases | volume = 38 | issue = 7 | pages = 1211–1221 | date = July 2019 | pmid = 30945014 | pmc = 6570665 | doi = 10.1007/s10096-019-03539-6 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Guh AY, Kutty PK | title = Clostridioides difficile Infection | journal = Annals of Internal Medicine | volume = 169 | issue = 7 | pages = ITC49–ITC64 | date = October 2018 | pmid = 30285209 | pmc = 6524133 | doi = 10.7326/AITC201810020 }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Legionella pneumophila]]'' adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan [[legionelosis]], sebuah [[Infeksi saluran pernapasan|infeksi pernapasan]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Chahin A, Opal SM | title = Severe Pneumonia Caused by Legionella pneumophila: Differential Diagnosis and Therapeutic Considerations | journal = Infectious Disease Clinics of North America | volume = 31 | issue = 1 | pages = 111–121 | date = March 2017 | pmid = 28159171 | pmc = 7135102 | doi = 10.1016/j.idc.2016.10.009 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Berjeaud JM, Chevalier S, Schlusselhuber M, Portier E, Loiseau C, Aucher W, Lesouhaitier O, Verdon J | display-authors = 6 | title = Legionella pneumophila: The Paradox of a Highly Sensitive Opportunistic Waterborne Pathogen Able to Persist in the Environment | journal = Frontiers in Microbiology | volume = 7 | pages = 486 | date = 2016-04-08 | pmid = 27092135 | pmc = 4824771 | doi = 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00486 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Mycobacterium avium complex]]'' (MAC) adalah kelompok dua bakteri, ''M. avium'' dan ''M. intracellulare'', yang biasanya menginfeksi secara bersamaan dan mengakibatkan infeksi paru yang disebut [[infeksi Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Falkinham JO | title = ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex: Adherence as a way of life | journal = AIMS Microbiology | volume = 4 | issue = 3 | pages = 428–438 | date = 2018 | pmid = 31294225 | pmc = 6604937 | doi = 10.3934/microbiol.2018.3.428 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pan SW, Shu CC, Feng JY, Su WJ | title = Treatment for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease | journal = Journal of the Formosan Medical Association = Taiwan Yi Zhi | volume = 119 Suppl 1 | pages = S67–S75 | date = June 2020 | pmid = 32446754 | doi = 10.1016/j.jfma.2020.05.006 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Mycobacterium tuberculosis]]'' adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan [[tuberkulosis]], sebuah infeksi pernapasan.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gordon SV, Parish T | title = Microbe Profile: Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Humanity's deadly microbial foe | journal = Microbiology | volume = 164 | issue = 4 | pages = 437–439 | date = April 2018 | pmid = 29465344 | doi = 10.1099/mic.0.000601 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Pseudomonas aeruginosa]]'' adalah spesies bakteri yang dapat menyebabkan infeksi pernapasan dan sering diasosiasikan dengan [[fibrosis sistik]] dan infeksi nosokomial.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Pang Z, Raudonis R, Glick BR, Lin TJ, Cheng Z | title = Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies | journal = Biotechnology Advances | volume = 37 | issue = 1 | pages = 177–192 | date = January–February 2019 | pmid = 30500353 | doi = 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.013 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Salmonella]]'' adalah [[genus]] bakteri yang menyebabkan infeksi pencernaan.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lamas A, Miranda JM, Regal P, Vázquez B, Franco CM, Cepeda A | title = A comprehensive review of non-enterica subspecies of Salmonella enterica | journal = Microbiological Research | volume = 206 | pages = 60–73 | date = January 2018 | pmid = 29146261 | doi = 10.1016/j.micres.2017.09.010 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Staphylococcus aureus]]'' adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan infeksi kulit, [[sepsis]], dan kondisi patologis lainnya. Spesies ini telah mengalami evolusi hingga terdapat galur yang [[Resistansi obat|resistan terhadap obat]], termasuk [[MRSA]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Jenul C, Horswill AR | title = Regulation of ''Staphylococcus aureus'' Virulence | journal = Microbiology Spectrum | volume = 7 | issue = 2 | date = April 2019 | pmid = 30953424 | pmc = 6452892 | doi = 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0031-2018 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kong C, Neoh HM, Nathan S | title = Targeting Staphylococcus aureus Toxins: A Potential form of Anti-Virulence Therapy | journal = Toxins | volume = 8 | issue = 3 | pages = 72 | date = March 2016 | pmid = 26999200 | pmc = 4810217 | doi = 10.3390/toxins8030072 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Streptococcus pneumoniae]]'' adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan infeksi pernapasan.<ref name=":2" /> |
|||
* ''[[Streptococcus pyogenes]]'' (juga dikenal sebagai ''Streptococcus'' grup A) adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan berbagai kondisi patologis, termasuk [[impetigo]] dan [[faringitis streptokokus]], serta berbagai penyakit lain yang lebih serius.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Jespersen MG, Lacey JA, Tong SY, Davies MR | title = Global genomic epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes | journal = Infection, Genetics and Evolution | volume = 86 | pages = 104609 | date = December 2020 | pmid = 33147506 | doi = 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104609 | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Brouwer S, Barnett TC, Rivera-Hernandez T, Rohde M, Walker MJ | title = Streptococcus pyogenes adhesion and colonization | journal = FEBS Letters | volume = 590 | issue = 21 | pages = 3739–3757 | date = November 2016 | pmid = 27312939 | doi = 10.1002/1873-3468.12254 | hdl = 10033/619157 | s2cid = 205213711 | hdl-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
=== Fungi === |
|||
* ''[[Aspergillus]]'' adalah jamur yang diasosiasikan dengan infeksi pernapasan.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Latgé JP, Chamilos G | title = Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis in 2019 | journal = Clinical Microbiology Reviews | volume = 33 | issue = 1 | pages = e00140–18, /cmr/33/1/CMR.00140–18.atom | date = December 2019 | pmid = 31722890 | pmc = 6860006 | doi = 10.1128/CMR.00140-18 }}</ref><ref name=":3">{{cite journal | vauthors = José RJ, Periselneris JN, Brown JS | title = Opportunistic bacterial, viral and fungal infections of the lung | journal = Medicine | volume = 48 | issue = 6 | pages = 366–372 | date = June 2020 | pmid = 32390758 | pmc = 7206443 | doi = 10.1016/j.mpmed.2020.03.006 }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Candida albicans]]'' adalah spesies jamur yang diasosiasikan dengan [[Oral candidiasis|oral thrush]] dan infeksi pencernaan.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Akpan A, Morgan R | title = Oral candidiasis | journal = Postgraduate Medical Journal | volume = 78 | issue = 922 | pages = 455–9 | date = August 2002 | pmid = 12185216 | pmc = 1742467 | doi = 10.1136/pmj.78.922.455 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Erdogan A, Rao SS | title = Small intestinal fungal overgrowth | journal = Current Gastroenterology Reports | volume = 17 | issue = 4 | pages = 16 | date = April 2015 | pmid = 25786900 | doi = 10.1007/s11894-015-0436-2 | s2cid = 3098136 }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Coccidioides immitis]]'' adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan [[koksidiomikosis]] yang lebih dikenal dengan demam lembah.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mu A, Shein TT, Jayachandran P, Paul S | title = Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Patients with AIDS and Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature | journal = Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care | volume = 16 | issue = 6 | pages = 540–545 | date = 2017-09-14 | pmid = 28911256 | doi = 10.1177/2325957417729751 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Cryptococcus neoformans]]'' adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan [[kriptokokosis]] yang dapat berkembang menjadi infeksi paru dan infeksi sistem saraf, seperti [[meningitis]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kwon-Chung KJ, Fraser JA, Doering TL, Wang Z, Janbon G, Idnurm A, Bahn YS | title = Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii, the etiologic agents of cryptococcosis | journal = Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine | volume = 4 | issue = 7 | pages = a019760 | date = July 2014 | pmid = 24985132 | pmc = 4066639 | doi = 10.1101/cshperspect.a019760 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Maziarz EK, Perfect JR | title = Cryptococcosis | journal = Infectious Disease Clinics of North America | volume = 30 | issue = 1 | pages = 179–206 | date = March 2016 | pmid = 26897067 | pmc = 5808417 | doi = 10.1016/j.idc.2015.10.006 }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Histoplasma capsulatum]]'' adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan [[histoplasmosis]], dengan berbagai manifestasi klinis, tetapi pada umumnya melibatkan sistem pernapasan.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Horwath MC, Fecher RA, Deepe GS | title = Histoplasma capsulatum, lung infection and immunity | journal = Future Microbiology | volume = 10 | issue = 6 | pages = 967–75 | date = 2015-06-10 | pmid = 26059620 | pmc = 4478585 | doi = 10.2217/fmb.15.25 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mittal J, Ponce MG, Gendlina I, Nosanchuk JD | title = Histoplasma Capsulatum: Mechanisms for Pathogenesis | journal = Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology | volume = 422 | pages = 157–191 | date = 2018 | pmid = 30043340 | pmc = 7212190 | doi = 10.1007/82_2018_114 | publisher = Springer International Publishing | isbn = 978-3-030-30236-8 | place = Cham | veditors = Rodrigues ML }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Pseudogymnoascus destructans]]'' (dulu dikenal sebagai ''Geomyces destructans'') adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan [[sindrom hidung putih]] pada kelelawar.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Seyedmousavi S, Bosco SM, de Hoog S, Ebel F, Elad D, Gomes RR, Jacobsen ID, Jensen HE, Martel A, Mignon B, Pasmans F, Piecková E, Rodrigues AM, Singh K, Vicente VA, Wibbelt G, Wiederhold NP, Guillot J | display-authors = 6 | title = Fungal infections in animals: a patchwork of different situations | journal = Medical Mycology | volume = 56 | issue = suppl_1 | pages = 165–187 | date = April 2018 | pmid = 29538732 | pmc = 6251577 | doi = 10.1093/mmy/myx104 }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Microsporidia]]'' adalah kelompok jamur yang menginfeksi beragam takson dalam kerajaan hewan; salah satu spesiesnya menyebabkan [[mikrosporodiosis]] pada manusia dengan sistem imun yang lemah.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Stentiford GD, Becnel JJ, Weiss LM, Keeling PJ, Didier ES, Bjornson S, Freeman MA, Brown MJ, Roesel K, Sokolova Y, Snowden KF, Solter L | display-authors = 6 | title = Microsporidia - Emergent Pathogens in the Global Food Chain | journal = Trends in Parasitology | volume = 32 | issue = 4 | pages = 336–348 | date = April 2016 | pmid = 26796229 | pmc = 4818719 | doi = 10.1016/j.pt.2015.12.004 }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Pneumocystis jirovecii]]'' (dulu dikenal sebagai ''Pneumocystis carinii'') adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan [[pneumonia pneumosistis]], sebuah infeksi pernapasan.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Sokulska M, Kicia M, Wesołowska M, Hendrich AB | title = Pneumocystis jirovecii--from a commensal to pathogen: clinical and diagnostic review | journal = Parasitology Research | volume = 114 | issue = 10 | pages = 3577–85 | date = October 2015 | pmid = 26281787 | pmc = 4562001 | doi = 10.1007/s00436-015-4678-6 }}</ref> |
|||
=== Parasit === |
|||
* ''[[Cryptosporidium]]'' adalah genus [[protozoa]] yang menginfeksi saluran pencernaan.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gerace E, Lo Presti VD, Biondo C | title = ''Cryptosporidium'' Infection: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Differential Diagnosis | journal = European Journal of Microbiology & Immunology | volume = 9 | issue = 4 | pages = 119–123 | date = December 2019 | pmid = 31934363 | pmc = 6945992 | doi = 10.1556/1886.2019.00019 }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Toxoplasma gondii]]'' adalah spesies protozoa yang menyebabkan [[toksoplasmosis]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Mendez OA, Koshy AA | title = Toxoplasma gondii: Entry, association, and physiological influence on the central nervous system | journal = PLOS Pathogens | volume = 13 | issue = 7 | pages = e1006351 | date = July 2017 | pmid = 28727854 | pmc = 5519211 | doi = 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006351 | veditors = Gubbels MJ }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hunter CA, Sibley LD | title = Modulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii virulence effectors | journal = Nature Reviews. Microbiology | volume = 10 | issue = 11 | pages = 766–78 | date = November 2012 | pmid = 23070557 | pmc = 3689224 | doi = 10.1038/nrmicro2858 }}</ref> |
|||
=== Virus === |
|||
* ''[[Cytomegalovirus]]'' adalah famili virus oportunistik yang sering diasosiasikan dengan infeksi pernapasan.<ref name=":3" /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Fonseca Brito L, Brune W, Stahl FR | title = Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Pneumonitis: Cell Tropism, Inflammation, and Immunity | journal = International Journal of Molecular Sciences | volume = 20 | issue = 16 | pages = 3865 | date = August 2019 | pmid = 31398860 | pmc = 6719013 | doi = 10.3390/ijms20163865 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Human polyomavirus 2]]'' (juga dikenal sebagai virus JC) adalah spesies virus yang menyebabkan [[leukoensefalopati multifokal progresif]] (PML).<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bohra C, Sokol L, Dalia S | title = Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy and Monoclonal Antibodies: A Review | journal = Cancer Control | volume = 24 | issue = 4 | pages = 1073274817729901 | date = 2017-11-01 | pmid = 28975841 | pmc = 5937251 | doi = 10.1177/1073274817729901 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Kartau M, Sipilä JO, Auvinen E, Palomäki M, Verkkoniemi-Ahola A | title = Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy: Current Insights | journal = Degenerative Neurological and Neuromuscular Disease | volume = 9 | pages = 109–121 | date = 2019-12-02 | pmid = 31819703 | pmc = 6896915 | doi = 10.2147/DNND.S203405 }}</ref> |
|||
* ''[[Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus|Human herpesvirus 8]]'' adalah spesies virus yang diasosiasikan dengan [[sarkoma Kaposi]], salah satu tipe kanker.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Radu O, Pantanowitz L | title = Kaposi sarcoma | journal = Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine | volume = 137 | issue = 2 | pages = 289–94 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23368874 | doi = 10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS | doi-access = free }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, Martin J, Bower M, Whitby D | title = Kaposi sarcoma | journal = Nature Reviews. Disease Primers | volume = 5 | issue = 1 | pages = 9 | date = January 2019 | pmid = 30705286 | pmc = 6685213 | doi = 10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9 }}</ref> |
|||
== Penyebab == |
== Penyebab == |
||
| Baris 16: | Baris 49: | ||
* Perawatan [[antibiotik]] |
* Perawatan [[antibiotik]] |
||
* Prosedur medikal |
* Prosedur medikal |
||
== Tipe infeksi == |
|||
* [[Pneumocystis pneumonia|''Pneumocystis jirovecii'']], dulunya dikenal sebagai [[Pneumocystis pneumonia|''Pneumocystis carinii'' f. ''hominis'']] |
|||
* ''[[Candida albicans]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Staphylococcus aureus]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Streptococcus pyogenes]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Pseudomonas aeruginosa]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Acinetobacter baumanni]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Toxoplasma gondii]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Cytomegalovirus]]'' |
|||
* ''[[Aspergillus]]'' sp. |
|||
* ''[[Sarkoma Kaposi]]'' |
|||
== Perawatan == |
|||
Perawatan bergantung pada tipe infeksi oportunistik, tetapi biasanya mengikutsertakan [[antibiotik]] yang berbeda. |
|||
== Referensi == |
== Referensi == |
||
Revisi per 12 Januari 2023 04.04
| Infeksi oportunistik | |
|---|---|
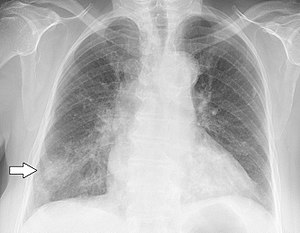 | |
| Gambaran sinar-X seseorang yang pada awalnya menderita influenza dan kemudian berkembang menjadi pneumonia akibat infeksi Haemophilus influenzae, yang diduga bersifat oportunistik | |
| Informasi umum | |
| Spesialisasi | Penyakit menular |
Infeksi oportunistik adalah infeksi yang disebabkan oleh organisme (seperti bakteri, jamur, parasit, atau virus) yang memanfaatkan kesempatan yang biasanya tidak tersedia. Kesempatan ini dapat berupa sistem imun yang melemah (misalnya akibat AIDS atau pemberian obat imunosupresif, seperti pada perawatan kanker),[1] perubahan mikrobioma (seperti gangguan pada mikrobiota usus), atau kerusakan pada sistem integumen (seperti pada trauma tajam). Banyak di antara organisme-organisme ini yang tidak menyebabkan penyakit pada inang sehat dengan sistem imun yang baik, dan dalam beberapa kasus, mereka berperan sebagai komensal sampai keseimbangan sistem imun terganggu.[2][3] Suatu infeksi juga dapat disebut oportunistik jika suatu patogen menyebabkan penyakit ringan pada orang sehat, tetapi menyebabkan penyakit yang lebih serius saat kondisi tubuh inangnya memungkinkan.[4]
Organisme oportunistik
Berbagai macam patogen terlibat dalam infeksi oportunistik dan dapat menyebabkan berbagai kondisi patologis. Berikut ini beberapa patogen oportunistik dan kondisi yang ditimbulkannya.
Bakteri
- Clostridioides difficile (dulu dikenal sebagai Clostridium difficile) adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan infeksi pencernaan dan umumnya diasosiasikan dengan infeksi nosokomial.[5][6]
- Legionella pneumophila adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan legionelosis, sebuah infeksi pernapasan.[7][8]
- Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) adalah kelompok dua bakteri, M. avium dan M. intracellulare, yang biasanya menginfeksi secara bersamaan dan mengakibatkan infeksi paru yang disebut infeksi Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare.[9][10]
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan tuberkulosis, sebuah infeksi pernapasan.[11]
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa adalah spesies bakteri yang dapat menyebabkan infeksi pernapasan dan sering diasosiasikan dengan fibrosis sistik dan infeksi nosokomial.[12]
- Salmonella adalah genus bakteri yang menyebabkan infeksi pencernaan.[13]
- Staphylococcus aureus adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan infeksi kulit, sepsis, dan kondisi patologis lainnya. Spesies ini telah mengalami evolusi hingga terdapat galur yang resistan terhadap obat, termasuk MRSA.[14][15]
- Streptococcus pneumoniae adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan infeksi pernapasan.[2]
- Streptococcus pyogenes (juga dikenal sebagai Streptococcus grup A) adalah spesies bakteri yang menyebabkan berbagai kondisi patologis, termasuk impetigo dan faringitis streptokokus, serta berbagai penyakit lain yang lebih serius.[16][17]
Fungi
- Aspergillus adalah jamur yang diasosiasikan dengan infeksi pernapasan.[18][19]
- Candida albicans adalah spesies jamur yang diasosiasikan dengan oral thrush dan infeksi pencernaan.[20][21]
- Coccidioides immitis adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan koksidiomikosis yang lebih dikenal dengan demam lembah.[22]
- Cryptococcus neoformans adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan kriptokokosis yang dapat berkembang menjadi infeksi paru dan infeksi sistem saraf, seperti meningitis.[23][24]
- Histoplasma capsulatum adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan histoplasmosis, dengan berbagai manifestasi klinis, tetapi pada umumnya melibatkan sistem pernapasan.[25][26]
- Pseudogymnoascus destructans (dulu dikenal sebagai Geomyces destructans) adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan sindrom hidung putih pada kelelawar.[27]
- Microsporidia adalah kelompok jamur yang menginfeksi beragam takson dalam kerajaan hewan; salah satu spesiesnya menyebabkan mikrosporodiosis pada manusia dengan sistem imun yang lemah.[28]
- Pneumocystis jirovecii (dulu dikenal sebagai Pneumocystis carinii) adalah spesies jamur yang menyebabkan pneumonia pneumosistis, sebuah infeksi pernapasan.[29]
Parasit
- Cryptosporidium adalah genus protozoa yang menginfeksi saluran pencernaan.[30]
- Toxoplasma gondii adalah spesies protozoa yang menyebabkan toksoplasmosis.[31][32]
Virus
- Cytomegalovirus adalah famili virus oportunistik yang sering diasosiasikan dengan infeksi pernapasan.[19][33]
- Human polyomavirus 2 (juga dikenal sebagai virus JC) adalah spesies virus yang menyebabkan leukoensefalopati multifokal progresif (PML).[34][35]
- Human herpesvirus 8 adalah spesies virus yang diasosiasikan dengan sarkoma Kaposi, salah satu tipe kanker.[36][37]
Penyebab
- Kekurangan gizi
- Infeksi kambuh
- Agen penekan sistem imun untuk resipien transplantasi organ
- Kemoterapi untuk Kanker
- AIDS atau infeksi HIV
- Kecenderungan geneticka
- Kerusakan kulit
- Perawatan antibiotik
- Prosedur medikal
Referensi
- ^ Justiz Vaillant AA, Qurie A (2021). "Immunodeficiency". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29763203. Diakses tanggal 9 Maret 2021.
- ^ a b Schroeder MR, Stephens DS (2016). "Macrolide Resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae". Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 6: 98. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2016.00098
 . PMC 5030221
. PMC 5030221  . PMID 27709102.
. PMID 27709102.
- ^ Achermann Y, Goldstein EJ, Coenye T, Shirtliff ME (2014). "Propionibacterium acnes: from commensal to opportunistic biofilm-associated implant pathogen". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 27 (3): 419–40. doi:10.1128/CMR.00092-13. PMC 4135900
 . PMID 24982315.
. PMID 24982315.
- ^ Caballero, Mauricio T.; Polack, Fernando P. (2018). "Respiratory syncytial virus is an "opportunistic" killer". Pediatric Pulmonology. 53 (5): 664–667. doi:10.1002/ppul.23963.
- ^ Czepiel J, Dróżdż M, Pituch H, Kuijper EJ, Perucki W, Mielimonka A, et al. (July 2019). "Clostridium difficile infection: review". European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 38 (7): 1211–1221. doi:10.1007/s10096-019-03539-6. PMC 6570665
 . PMID 30945014.
. PMID 30945014.
- ^ Guh AY, Kutty PK (October 2018). "Clostridioides difficile Infection". Annals of Internal Medicine. 169 (7): ITC49–ITC64. doi:10.7326/AITC201810020. PMC 6524133
 . PMID 30285209.
. PMID 30285209.
- ^ Chahin A, Opal SM (March 2017). "Severe Pneumonia Caused by Legionella pneumophila: Differential Diagnosis and Therapeutic Considerations". Infectious Disease Clinics of North America. 31 (1): 111–121. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2016.10.009. PMC 7135102
 . PMID 28159171.
. PMID 28159171.
- ^ Berjeaud JM, Chevalier S, Schlusselhuber M, Portier E, Loiseau C, Aucher W, et al. (2016-04-08). "Legionella pneumophila: The Paradox of a Highly Sensitive Opportunistic Waterborne Pathogen Able to Persist in the Environment". Frontiers in Microbiology. 7: 486. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.00486
 . PMC 4824771
. PMC 4824771  . PMID 27092135.
. PMID 27092135.
- ^ Falkinham JO (2018). "Mycobacterium avium complex: Adherence as a way of life". AIMS Microbiology. 4 (3): 428–438. doi:10.3934/microbiol.2018.3.428. PMC 6604937
 . PMID 31294225.
. PMID 31294225.
- ^ Pan SW, Shu CC, Feng JY, Su WJ (June 2020). "Treatment for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease". Journal of the Formosan Medical Association = Taiwan Yi Zhi. 119 Suppl 1: S67–S75. doi:10.1016/j.jfma.2020.05.006
 . PMID 32446754.
. PMID 32446754.
- ^ Gordon SV, Parish T (April 2018). "Microbe Profile: Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Humanity's deadly microbial foe". Microbiology. 164 (4): 437–439. doi:10.1099/mic.0.000601
 . PMID 29465344.
. PMID 29465344.
- ^ Pang Z, Raudonis R, Glick BR, Lin TJ, Cheng Z (January–February 2019). "Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mechanisms and alternative therapeutic strategies". Biotechnology Advances. 37 (1): 177–192. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.11.013
 . PMID 30500353.
. PMID 30500353.
- ^ Lamas A, Miranda JM, Regal P, Vázquez B, Franco CM, Cepeda A (January 2018). "A comprehensive review of non-enterica subspecies of Salmonella enterica". Microbiological Research. 206: 60–73. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2017.09.010
 . PMID 29146261.
. PMID 29146261.
- ^ Jenul C, Horswill AR (April 2019). "Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence". Microbiology Spectrum. 7 (2). doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0031-2018. PMC 6452892
 . PMID 30953424.
. PMID 30953424.
- ^ Kong C, Neoh HM, Nathan S (March 2016). "Targeting Staphylococcus aureus Toxins: A Potential form of Anti-Virulence Therapy". Toxins. 8 (3): 72. doi:10.3390/toxins8030072
 . PMC 4810217
. PMC 4810217  . PMID 26999200.
. PMID 26999200.
- ^ Jespersen MG, Lacey JA, Tong SY, Davies MR (December 2020). "Global genomic epidemiology of Streptococcus pyogenes". Infection, Genetics and Evolution. 86: 104609. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104609
 . PMID 33147506 Periksa nilai
. PMID 33147506 Periksa nilai |pmid=(bantuan). - ^ Brouwer S, Barnett TC, Rivera-Hernandez T, Rohde M, Walker MJ (November 2016). "Streptococcus pyogenes adhesion and colonization". FEBS Letters. 590 (21): 3739–3757. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.12254. hdl:10033/619157
 . PMID 27312939.
. PMID 27312939.
- ^ Latgé JP, Chamilos G (December 2019). "Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis in 2019". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 33 (1): e00140–18, /cmr/33/1/CMR.00140–18.atom. doi:10.1128/CMR.00140-18. PMC 6860006
 . PMID 31722890.
. PMID 31722890.
- ^ a b José RJ, Periselneris JN, Brown JS (June 2020). "Opportunistic bacterial, viral and fungal infections of the lung". Medicine. 48 (6): 366–372. doi:10.1016/j.mpmed.2020.03.006. PMC 7206443
 . PMID 32390758.
. PMID 32390758.
- ^ Akpan A, Morgan R (August 2002). "Oral candidiasis". Postgraduate Medical Journal. 78 (922): 455–9. doi:10.1136/pmj.78.922.455. PMC 1742467
 . PMID 12185216.
. PMID 12185216.
- ^ Erdogan A, Rao SS (April 2015). "Small intestinal fungal overgrowth". Current Gastroenterology Reports. 17 (4): 16. doi:10.1007/s11894-015-0436-2. PMID 25786900.
- ^ Mu A, Shein TT, Jayachandran P, Paul S (2017-09-14). "Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Patients with AIDS and Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature". Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care. 16 (6): 540–545. doi:10.1177/2325957417729751
 . PMID 28911256.
. PMID 28911256.
- ^ Kwon-Chung KJ, Fraser JA, Doering TL, Wang Z, Janbon G, Idnurm A, Bahn YS (July 2014). "Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii, the etiologic agents of cryptococcosis". Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine. 4 (7): a019760. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a019760. PMC 4066639
 . PMID 24985132.
. PMID 24985132.
- ^ Maziarz EK, Perfect JR (March 2016). "Cryptococcosis". Infectious Disease Clinics of North America. 30 (1): 179–206. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2015.10.006. PMC 5808417
 . PMID 26897067.
. PMID 26897067.
- ^ Horwath MC, Fecher RA, Deepe GS (2015-06-10). "Histoplasma capsulatum, lung infection and immunity". Future Microbiology. 10 (6): 967–75. doi:10.2217/fmb.15.25. PMC 4478585
 . PMID 26059620.
. PMID 26059620.
- ^ Mittal J, Ponce MG, Gendlina I, Nosanchuk JD (2018). Rodrigues ML, ed. "Histoplasma Capsulatum: Mechanisms for Pathogenesis". Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. Cham: Springer International Publishing. 422: 157–191. doi:10.1007/82_2018_114. ISBN 978-3-030-30236-8. PMC 7212190
 . PMID 30043340.
. PMID 30043340.
- ^ Seyedmousavi S, Bosco SM, de Hoog S, Ebel F, Elad D, Gomes RR, et al. (April 2018). "Fungal infections in animals: a patchwork of different situations". Medical Mycology. 56 (suppl_1): 165–187. doi:10.1093/mmy/myx104. PMC 6251577
 . PMID 29538732.
. PMID 29538732.
- ^ Stentiford GD, Becnel JJ, Weiss LM, Keeling PJ, Didier ES, Bjornson S, et al. (April 2016). "Microsporidia - Emergent Pathogens in the Global Food Chain". Trends in Parasitology. 32 (4): 336–348. doi:10.1016/j.pt.2015.12.004. PMC 4818719
 . PMID 26796229.
. PMID 26796229.
- ^ Sokulska M, Kicia M, Wesołowska M, Hendrich AB (October 2015). "Pneumocystis jirovecii--from a commensal to pathogen: clinical and diagnostic review". Parasitology Research. 114 (10): 3577–85. doi:10.1007/s00436-015-4678-6. PMC 4562001
 . PMID 26281787.
. PMID 26281787.
- ^ Gerace E, Lo Presti VD, Biondo C (December 2019). "Cryptosporidium Infection: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Differential Diagnosis". European Journal of Microbiology & Immunology. 9 (4): 119–123. doi:10.1556/1886.2019.00019. PMC 6945992
 . PMID 31934363.
. PMID 31934363.
- ^ Mendez OA, Koshy AA (July 2017). Gubbels MJ, ed. "Toxoplasma gondii: Entry, association, and physiological influence on the central nervous system". PLOS Pathogens. 13 (7): e1006351. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1006351. PMC 5519211
 . PMID 28727854.
. PMID 28727854.
- ^ Hunter CA, Sibley LD (November 2012). "Modulation of innate immunity by Toxoplasma gondii virulence effectors". Nature Reviews. Microbiology. 10 (11): 766–78. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2858. PMC 3689224
 . PMID 23070557.
. PMID 23070557.
- ^ Fonseca Brito L, Brune W, Stahl FR (August 2019). "Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Pneumonitis: Cell Tropism, Inflammation, and Immunity". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 20 (16): 3865. doi:10.3390/ijms20163865
 . PMC 6719013
. PMC 6719013  . PMID 31398860.
. PMID 31398860.
- ^ Bohra C, Sokol L, Dalia S (2017-11-01). "Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy and Monoclonal Antibodies: A Review". Cancer Control. 24 (4): 1073274817729901. doi:10.1177/1073274817729901. PMC 5937251
 . PMID 28975841.
. PMID 28975841.
- ^ Kartau M, Sipilä JO, Auvinen E, Palomäki M, Verkkoniemi-Ahola A (2019-12-02). "Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy: Current Insights". Degenerative Neurological and Neuromuscular Disease. 9: 109–121. doi:10.2147/DNND.S203405. PMC 6896915
 . PMID 31819703.
. PMID 31819703.
- ^ Radu O, Pantanowitz L (February 2013). "Kaposi sarcoma". Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. 137 (2): 289–94. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0101-RS
 . PMID 23368874.
. PMID 23368874.
- ^ Cesarman E, Damania B, Krown SE, Martin J, Bower M, Whitby D (January 2019). "Kaposi sarcoma". Nature Reviews. Disease Primers. 5 (1): 9. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0060-9. PMC 6685213
 . PMID 30705286.
. PMID 30705286.
